
Foundation Mathematics
1017SCG
Week 7
Topics for Week 7
- Graphing linear equations
- Finding the equation of a linear graph
- Graphing quadratic equations
- Solving simultaneous equations
Graphing linear equations
$y = 2x+1$
| $x$ | $-3$ | $-2$ | $-1$ | $0$ | $1$ | $2$ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $y$ | $-5$ | $-3$ | $-1$ | $1$ | $3$ | $5$ |
|
When $x=-3,$ $\quad y=2(-3)+1$ $\quad \;\;\,=-6+1$ $\quad \;\;\,=-5$ |
When $x=0,$ $\quad y=2(0)+1$ $\quad \;\;\,=0+1$ $\quad \;\;\,=1$ |
Graphing linear equations
Graphing linear equations
Linear Equation → Linear Graph
Standard Form:
$ax+ by + d = 0\,$ with $\,a,b,d$ constants.
Gradient-Intercept Form:
$y = mx + c\,$ with $\,m,c\,$ constants.
• $m$ is the gradient.
• $c$ is the $y$-intercept.
What is the Gradient? 🤔
👉 $y = mx + c$
$m= \text{gradient}$ $= \dfrac{\text{opp}}{\text{adj}}$ $= \tan \theta$
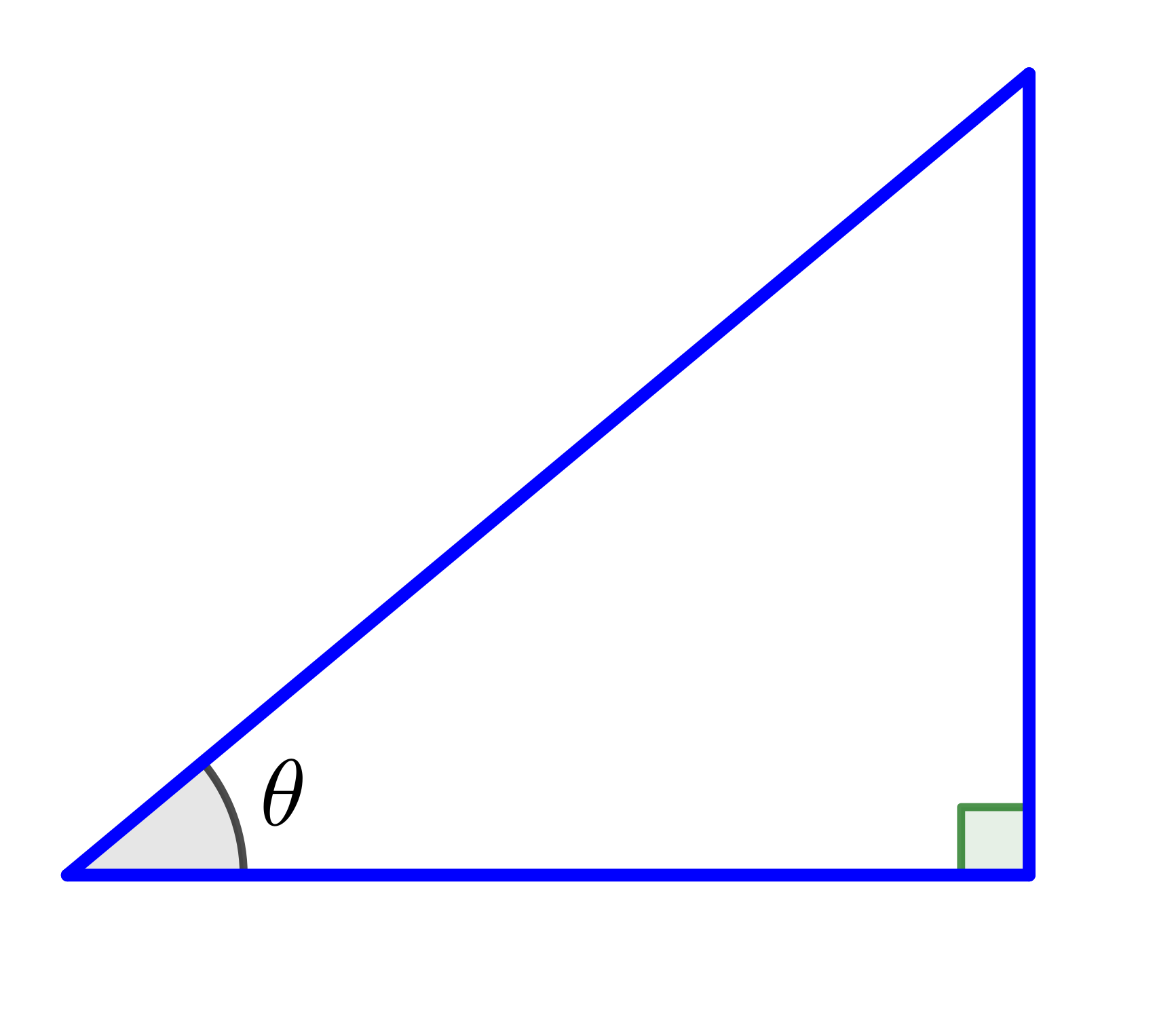
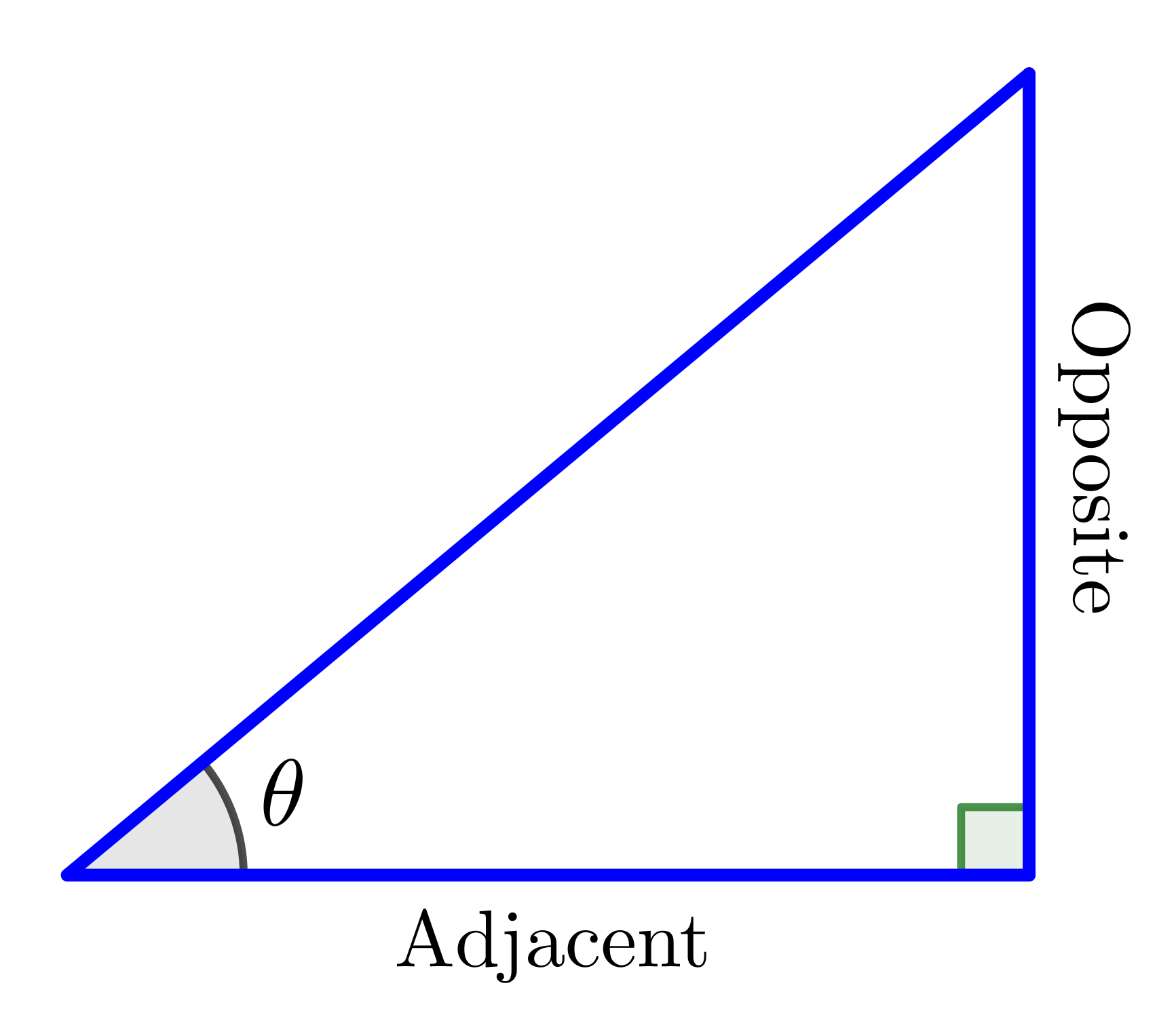
What is the Gradient? 🤔
👉 $y = mx + c$
$m= \text{gradient}$ $= \dfrac{\text{opp}}{\text{adj}}$ $= \tan \theta$
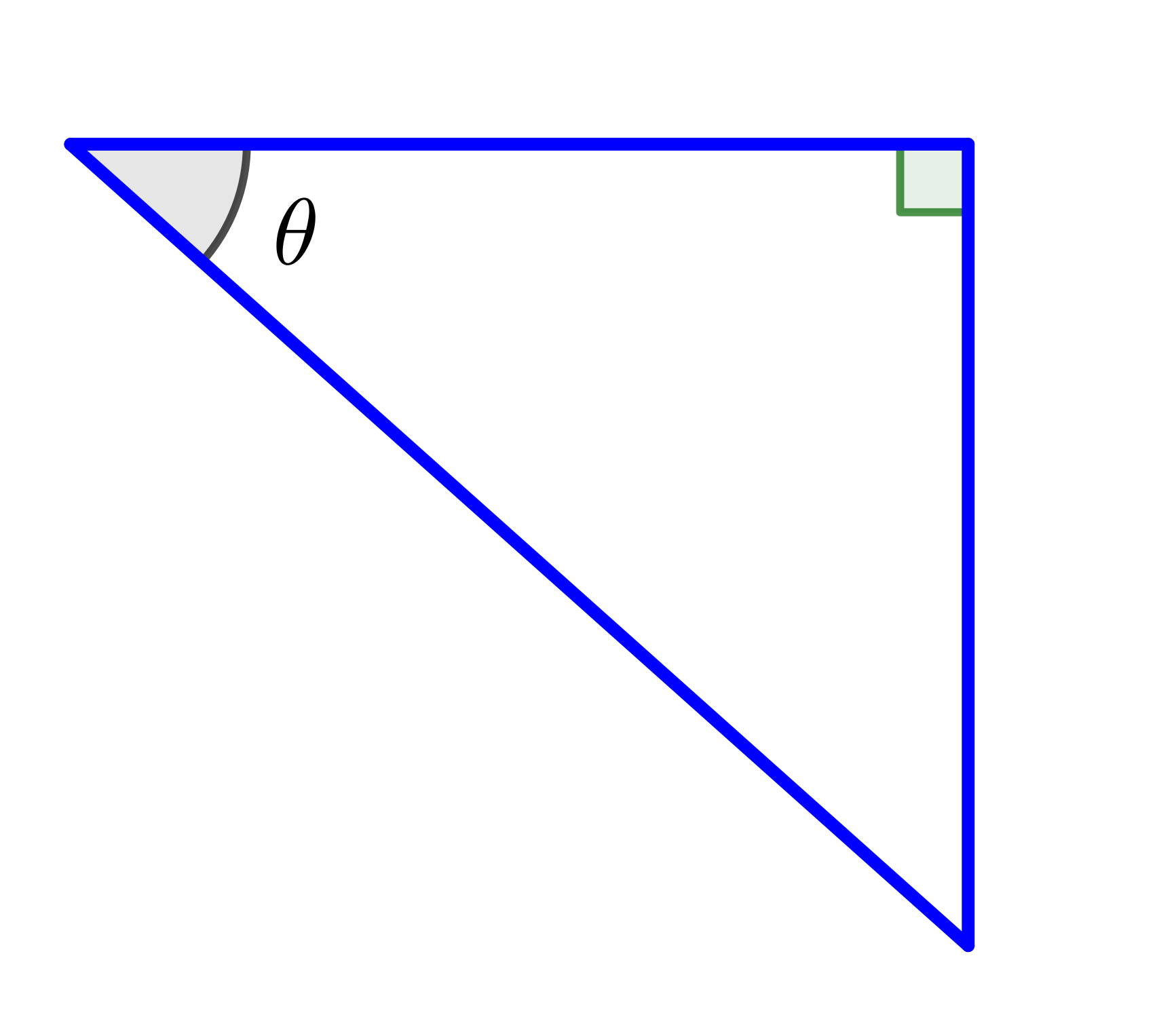
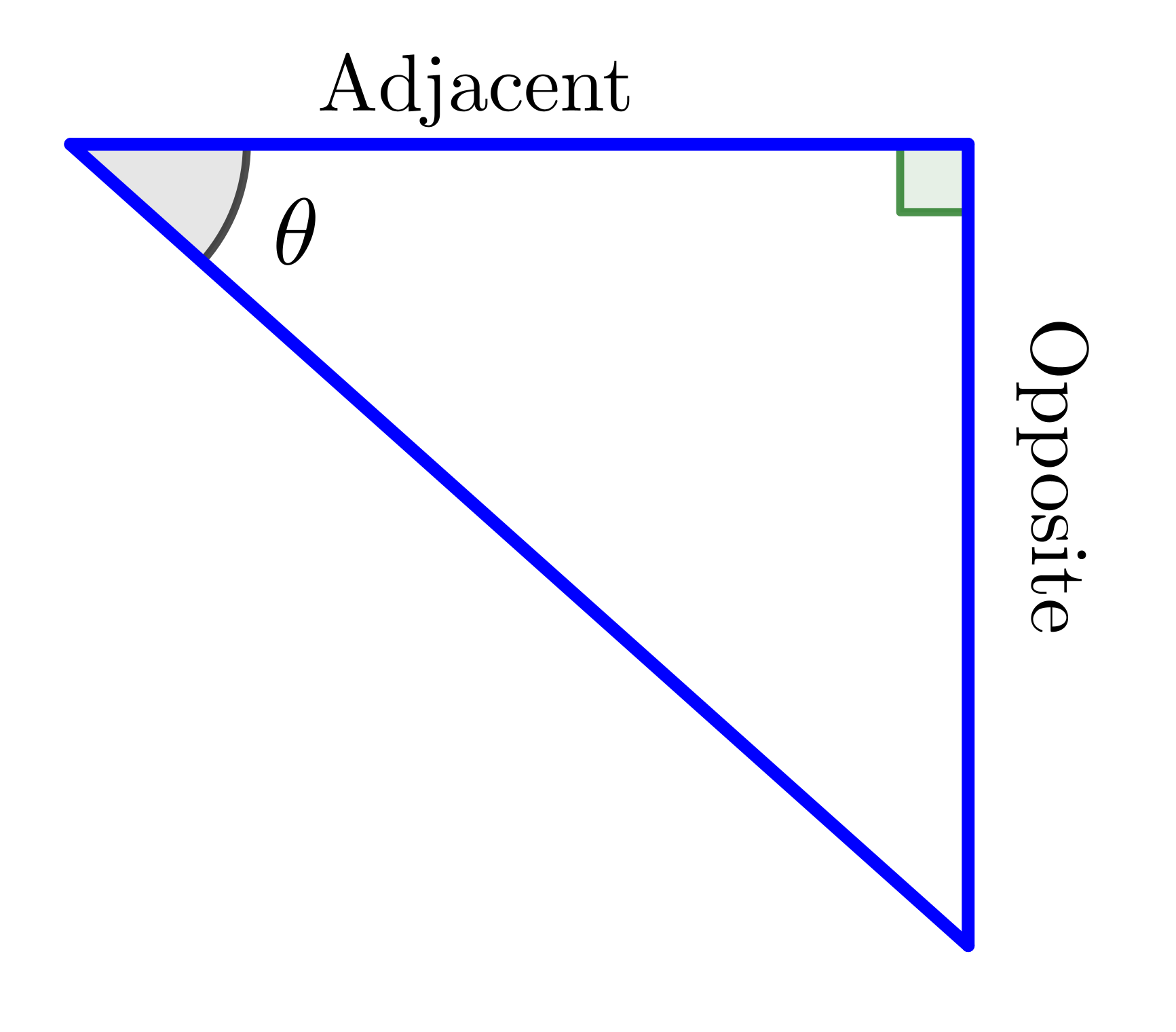
What is the Gradient? 🤔
👉 $y = mx + c$
| $\text{gradient}= \dfrac{\text{opp}}{\text{adj}}=\tan \theta$ |
| $\text{gradient}= \dfrac{\text{Change in }y}{\text{Change in } x}$ $=\dfrac{\Delta y}{\Delta x}$ |
The second expression is often used in science!

Example 1: $\,y=3x-3$
Example 1: $\,y=3x-3$
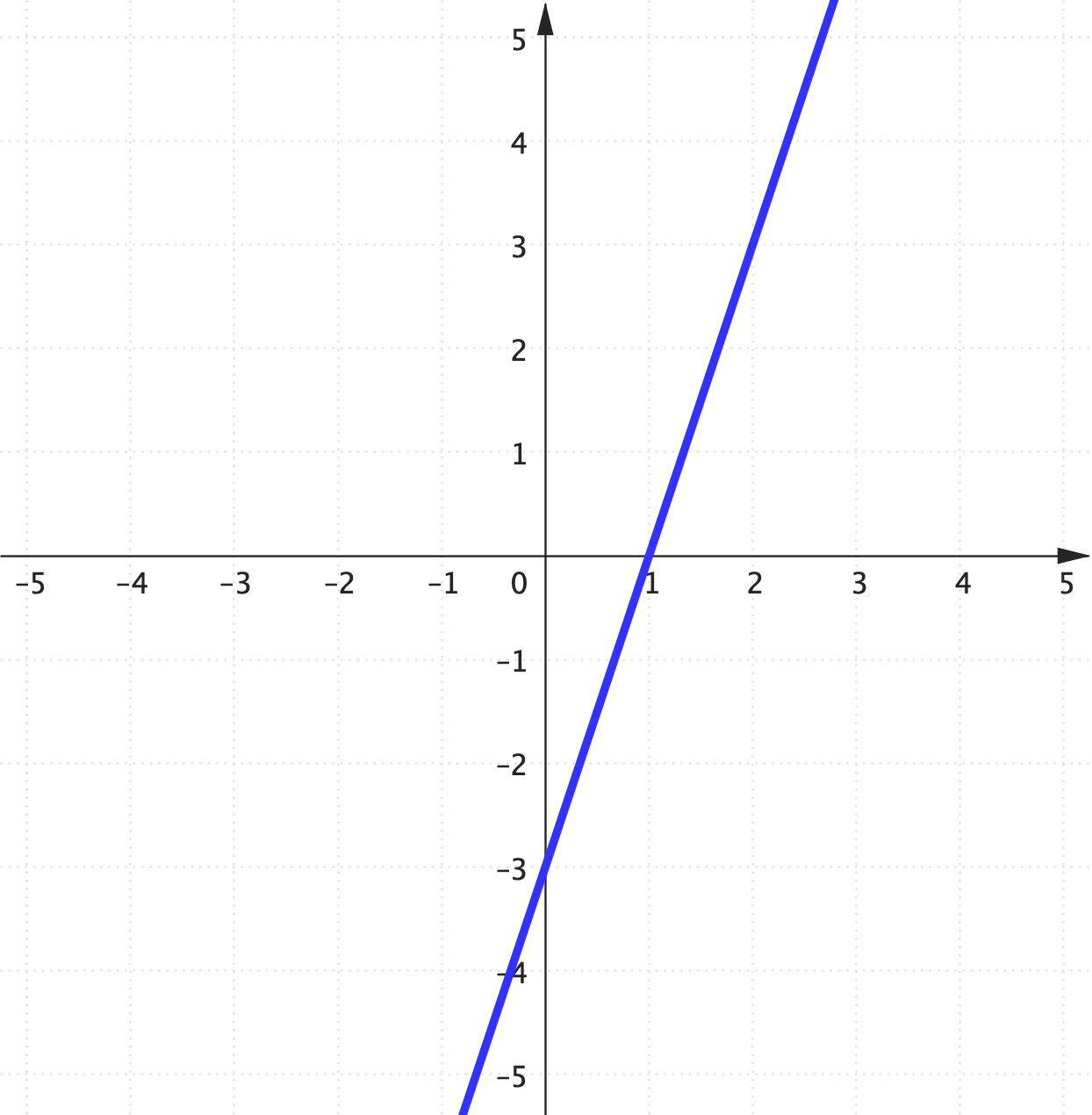
Example 2: $\,y=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+1$
Example 2: $\,y=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+1$
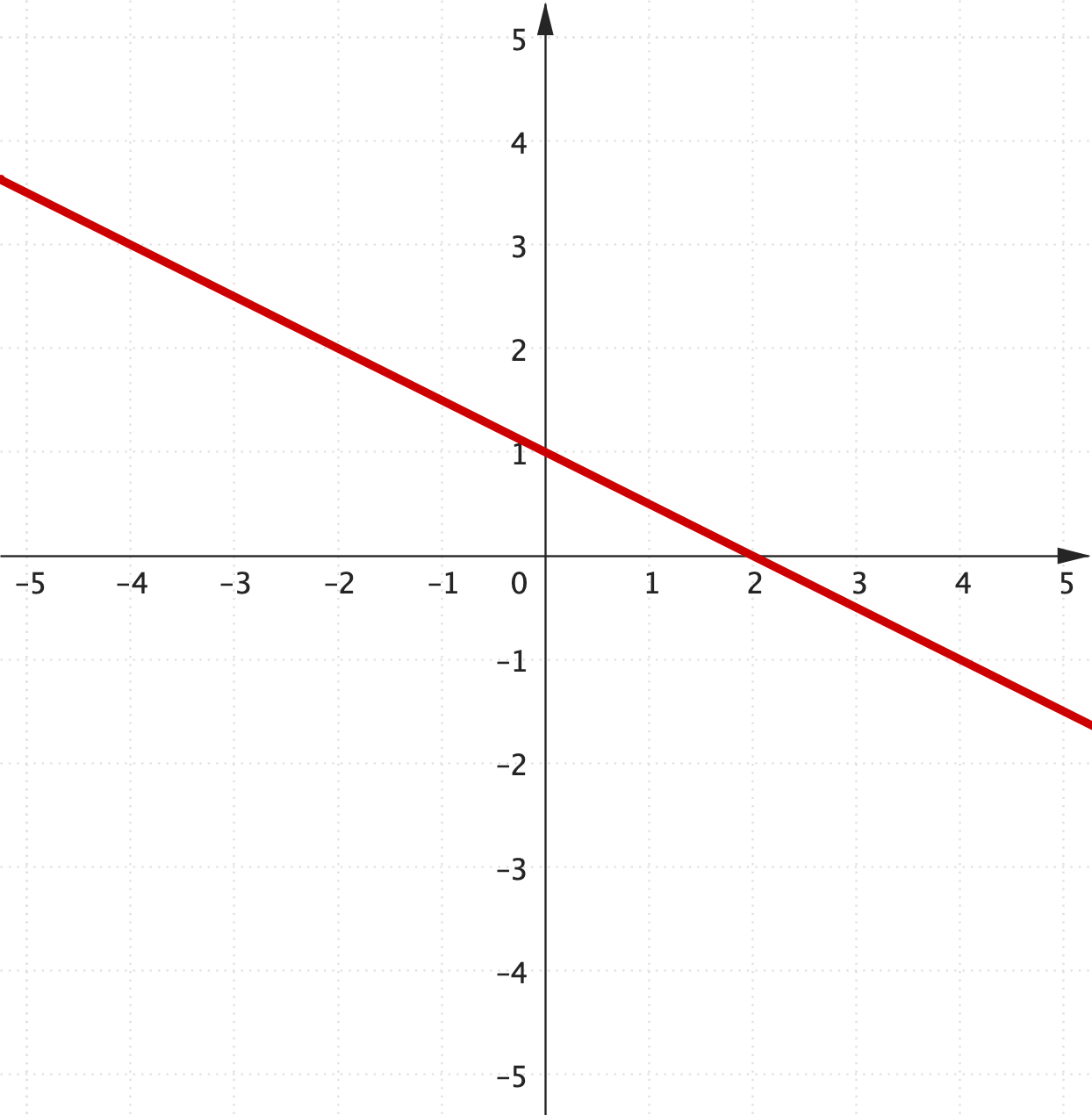
Example 3: Special cases
|
|
Case 1: $y=3$ $y=0\times x + 3$ Case 2: $x=-2$ |
Example 3: Special cases
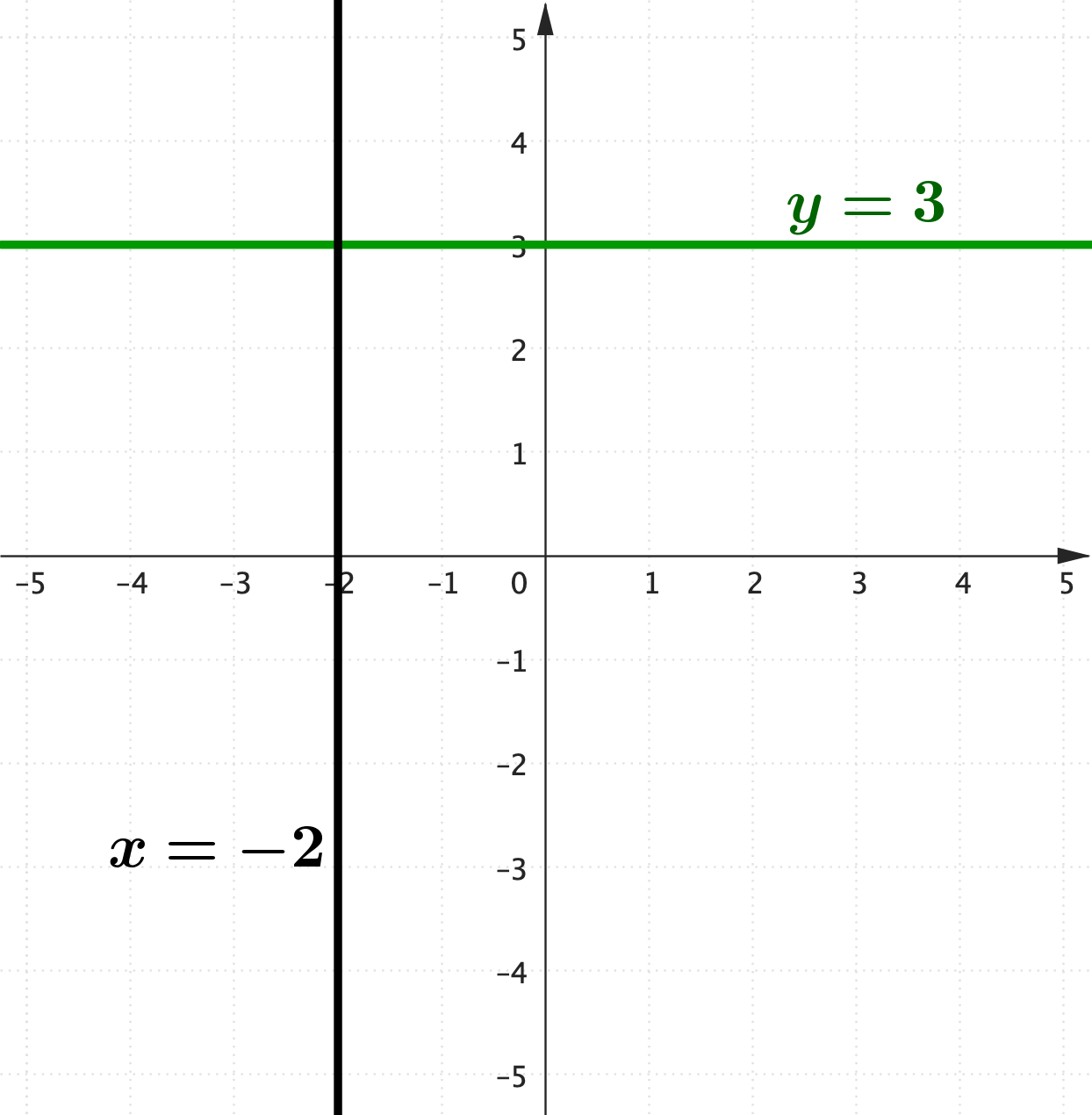
|
Case 1: $y=3$ $y=0\times x + 3$ Case 2: $x=-2$ |
Finding the Equation of a Line
Previously
|
Give the linear equation: $\;\;y=3x-3$ $\rightarrow$ |

|
Finding the Equation of a Line
How can we obtain the equation of any line? 🤔
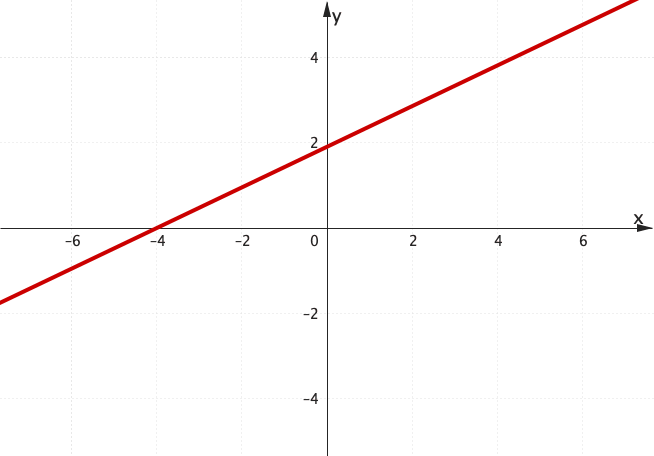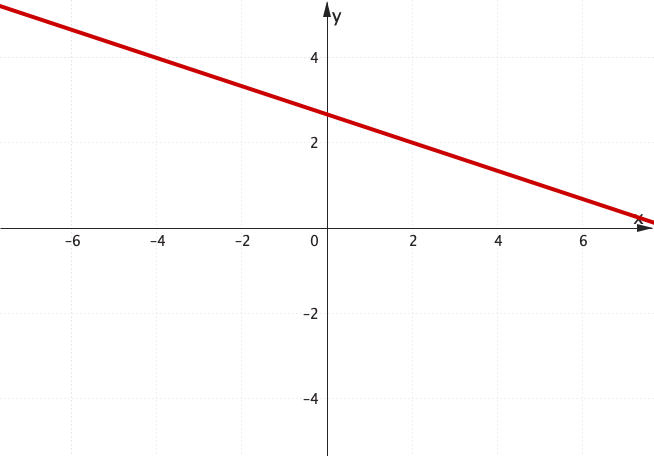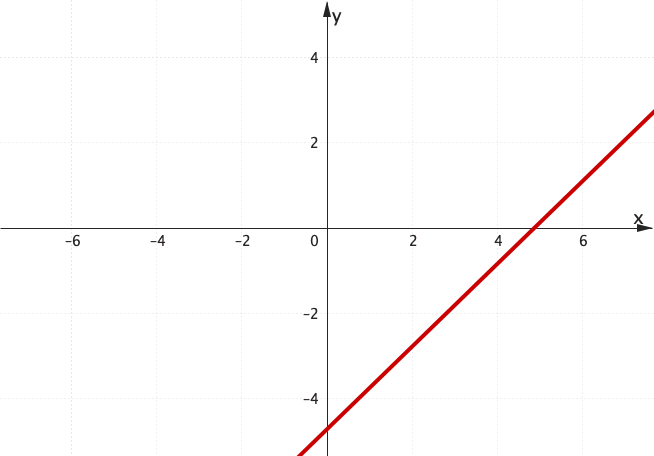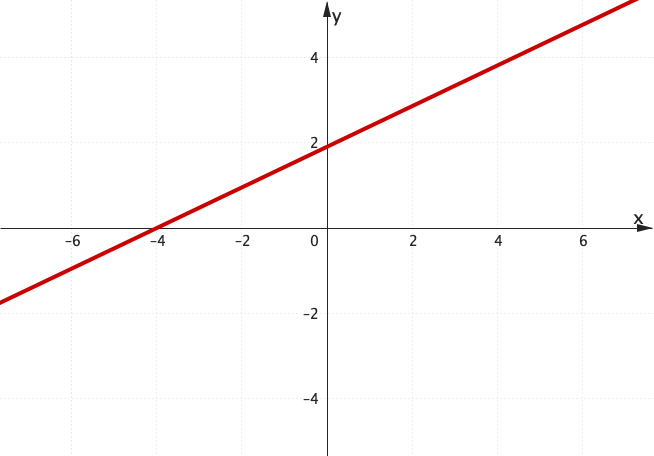
Finding the Equation of a Line
😃 Through 2 points, we can always draw a straight line!
Finding the Equation of a Line
Consider the following two points $(x_1,y_1)\,$ and $\,(x_2,y_2)$
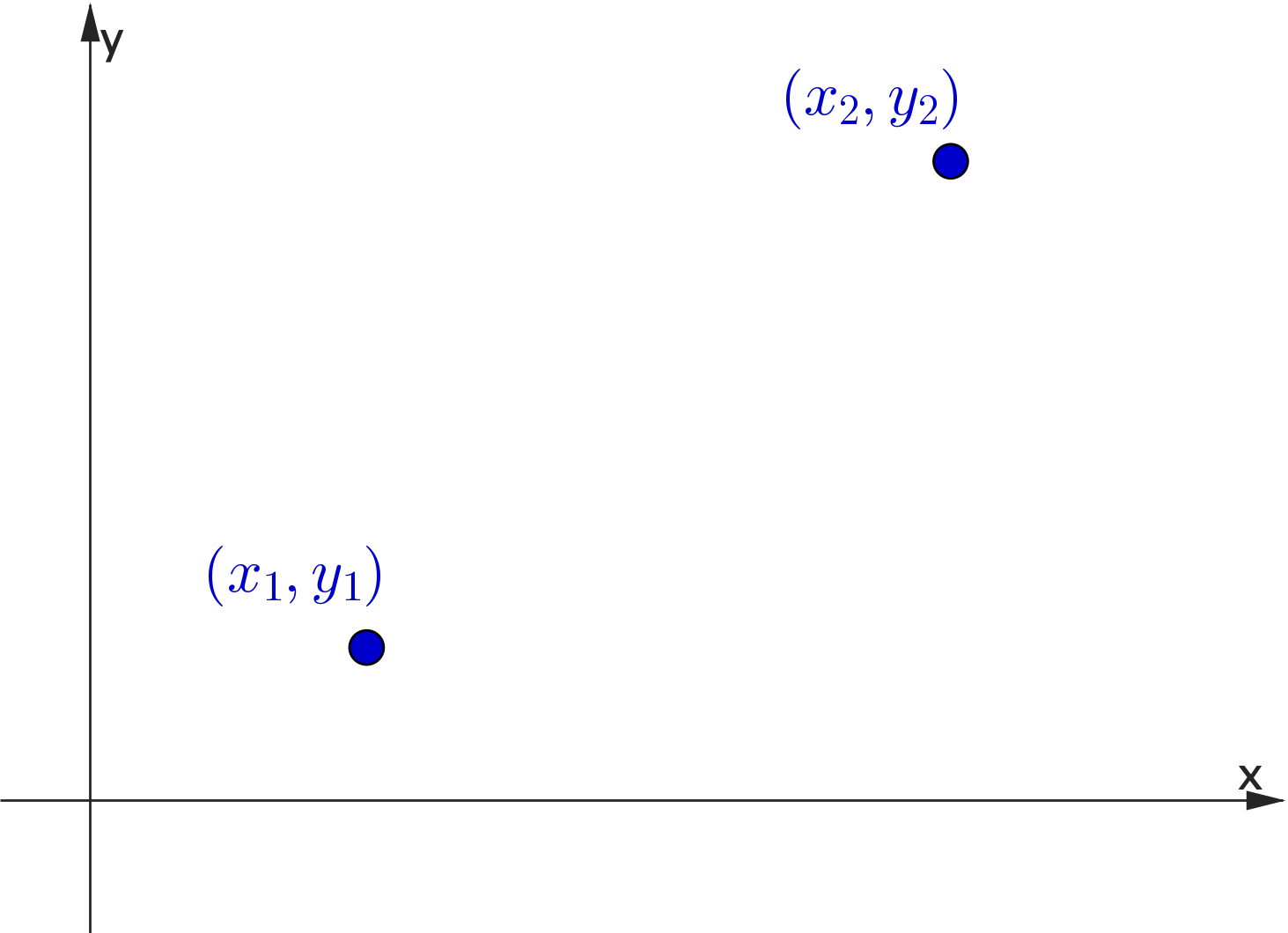
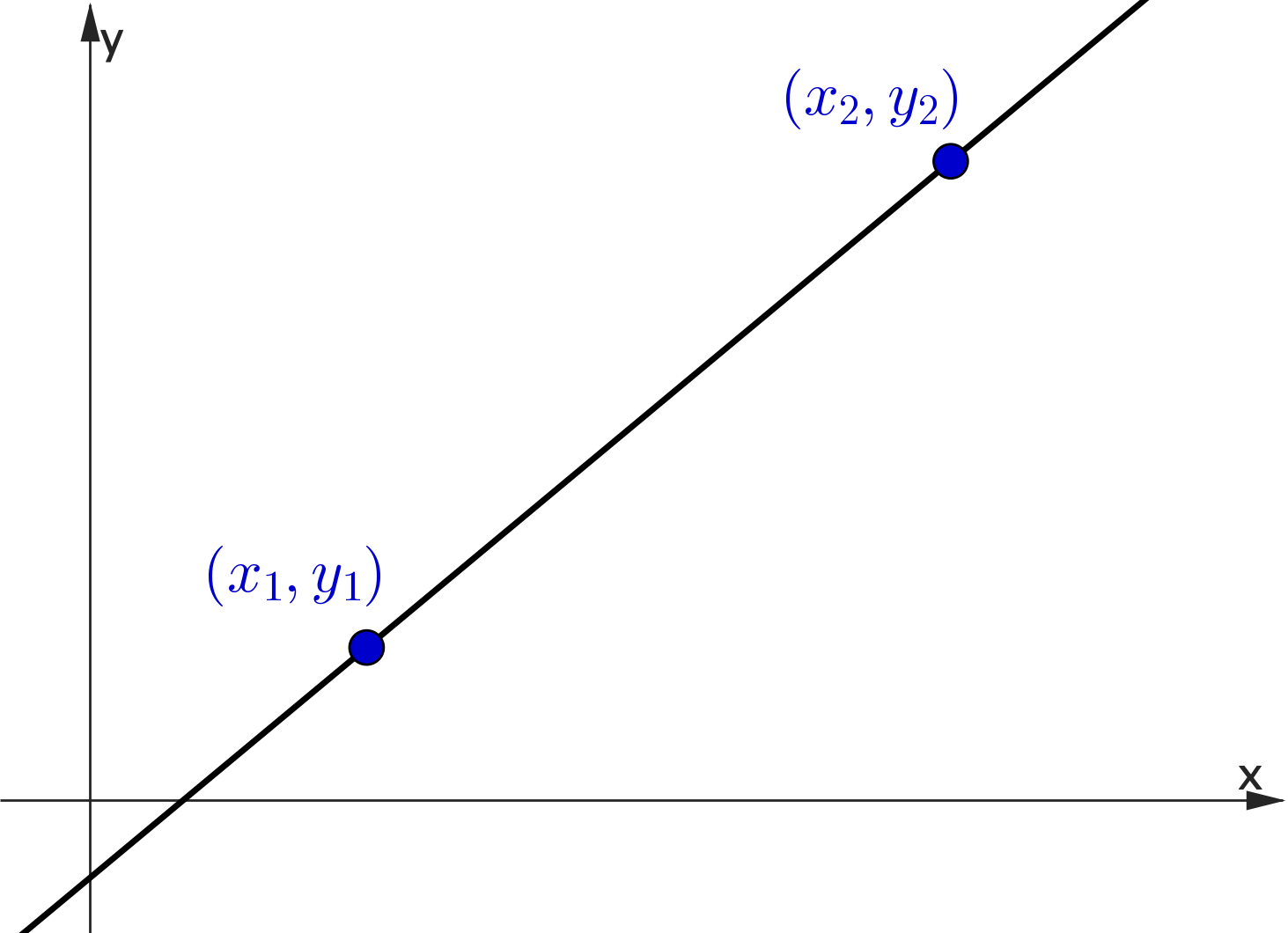
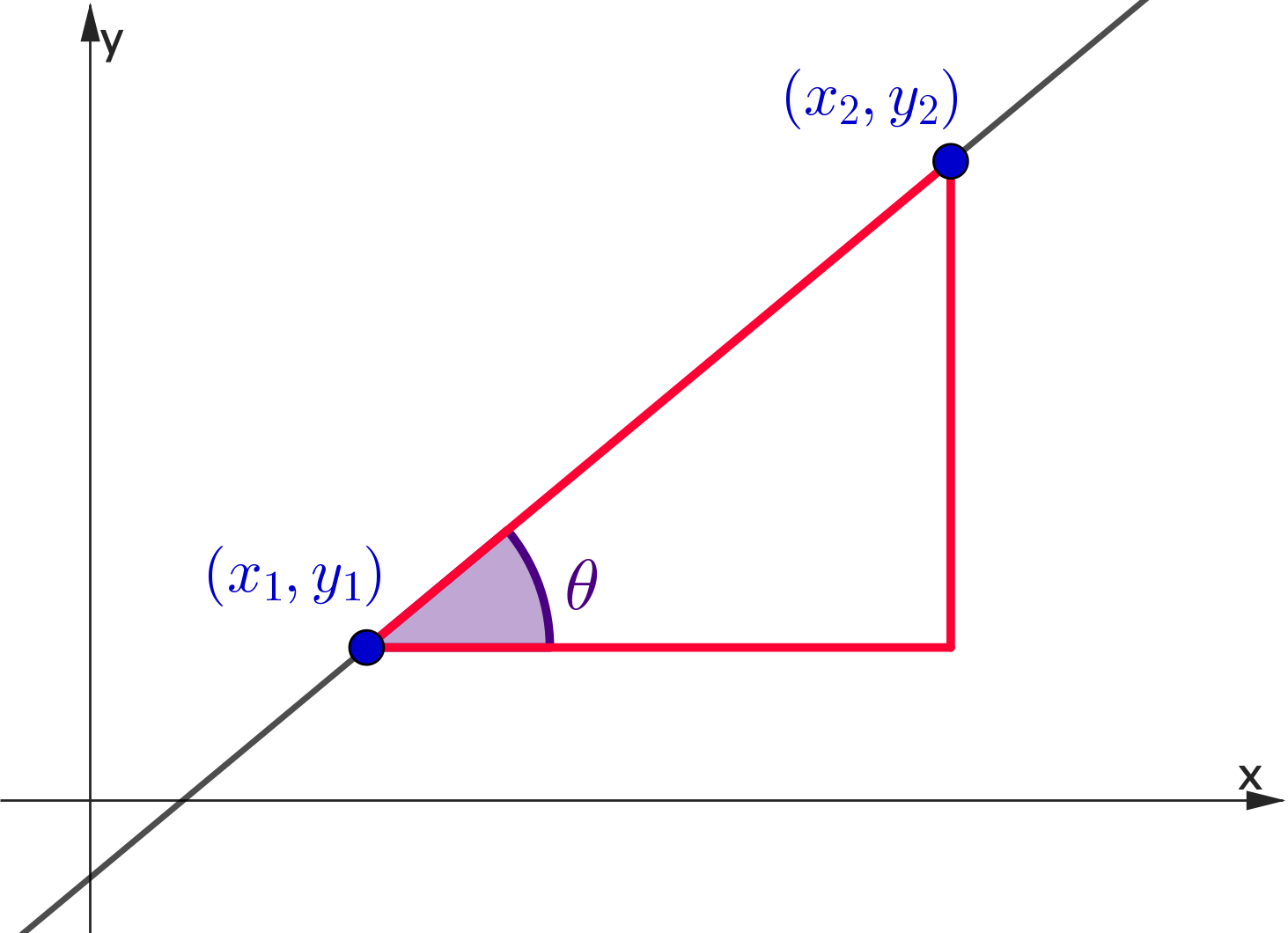
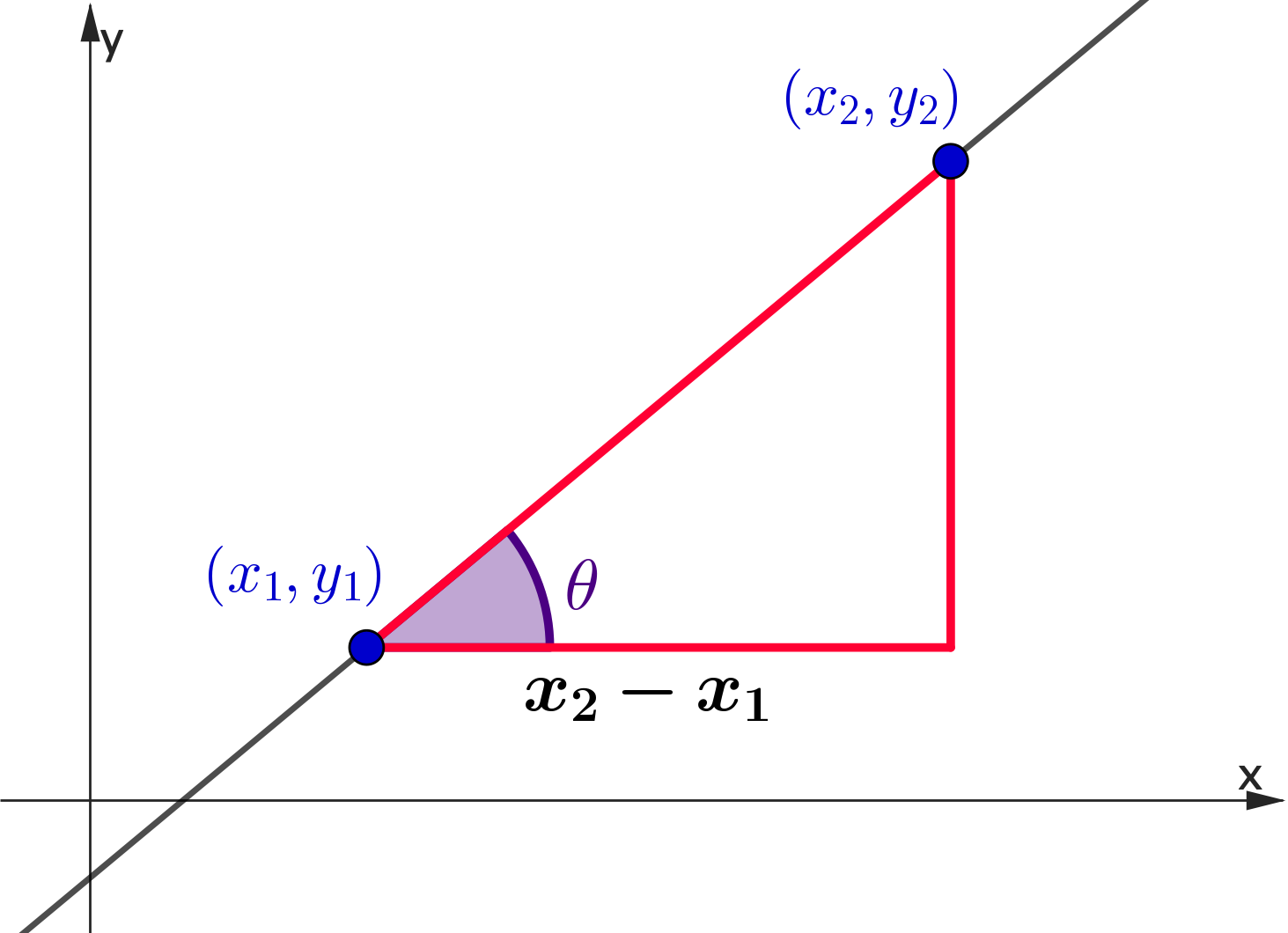
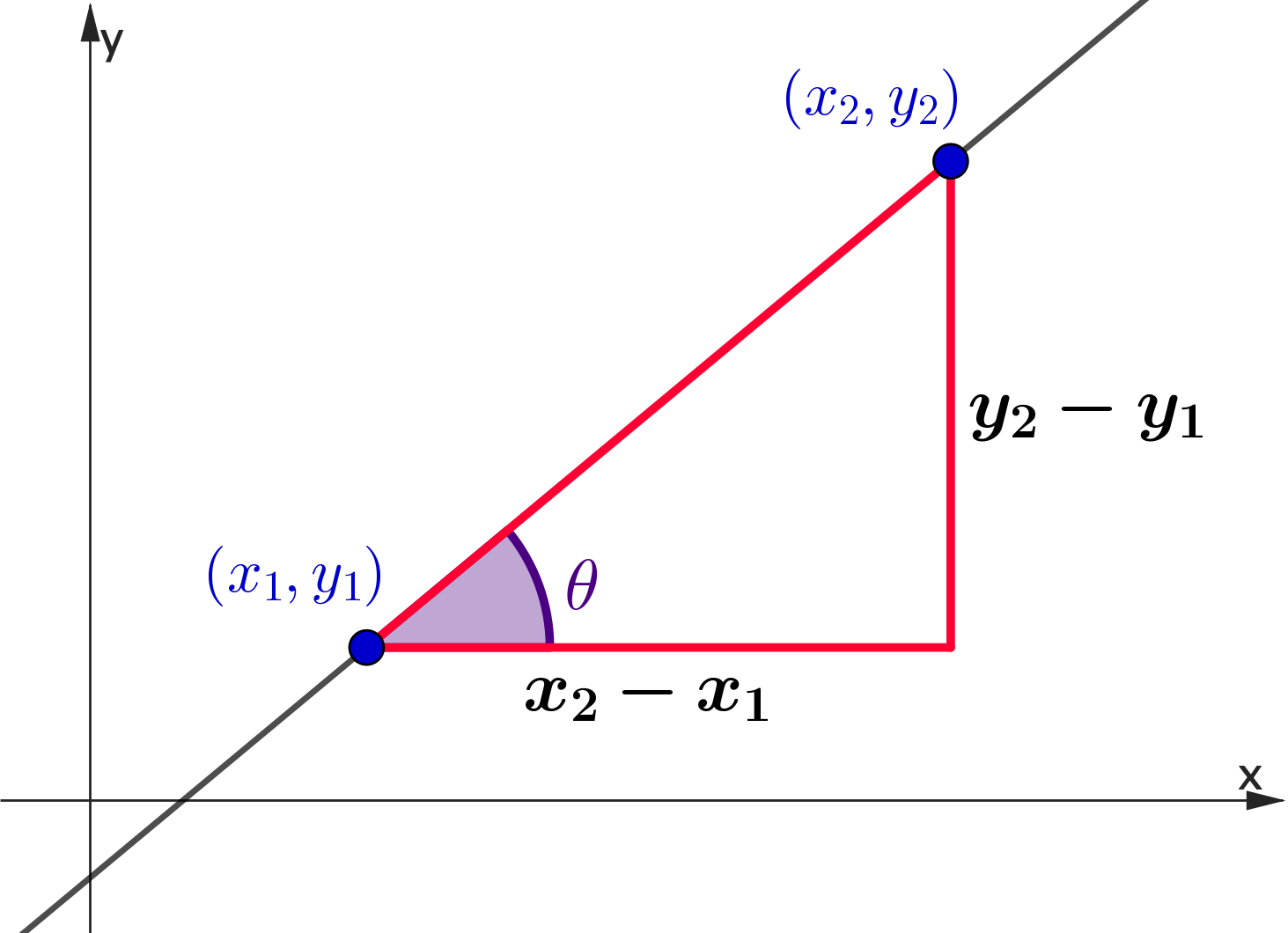
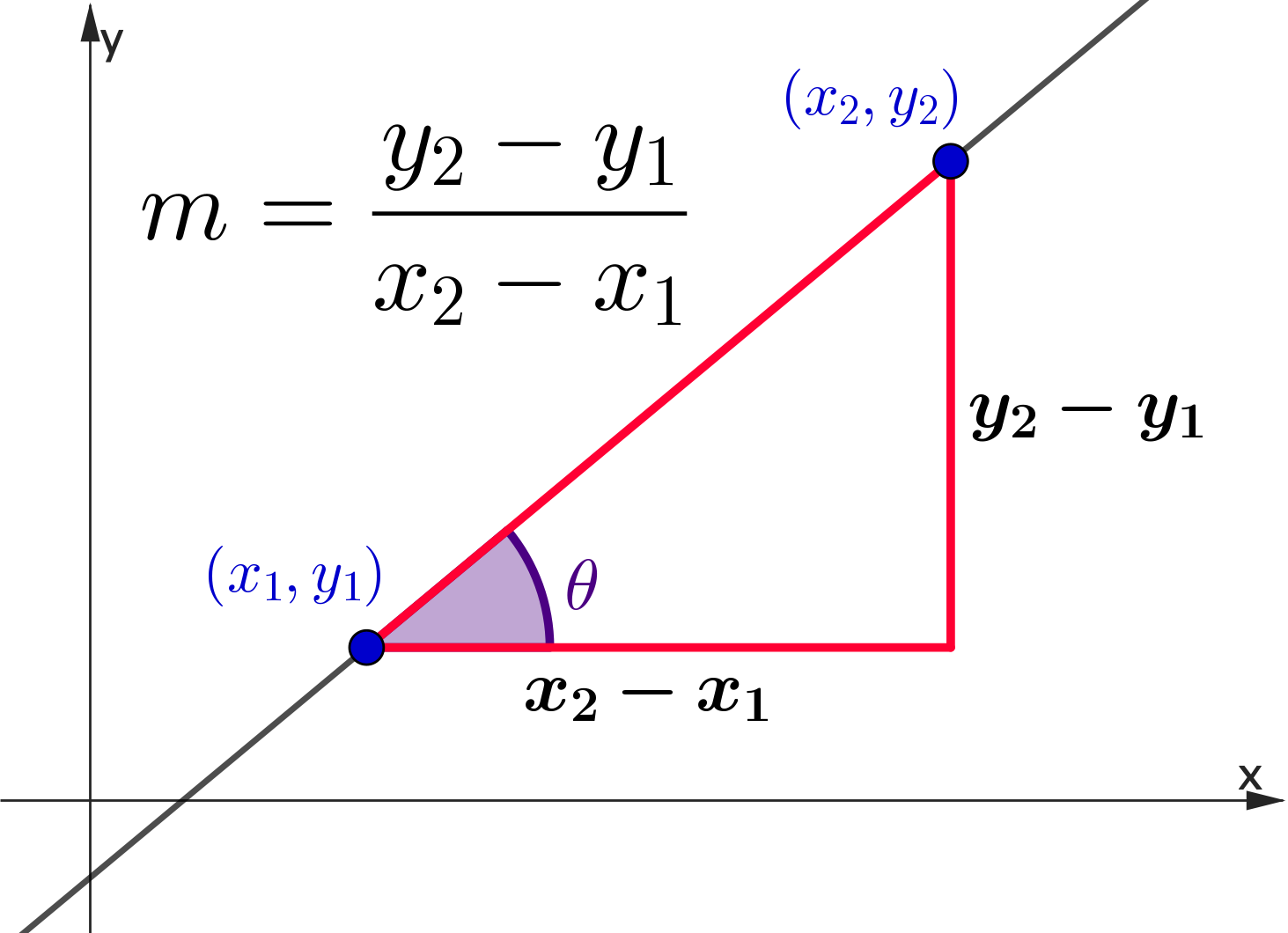
Finding the Equation of a Line
👉 Consider $(x_1,y_1)$ and any other point $\,(x,y)$
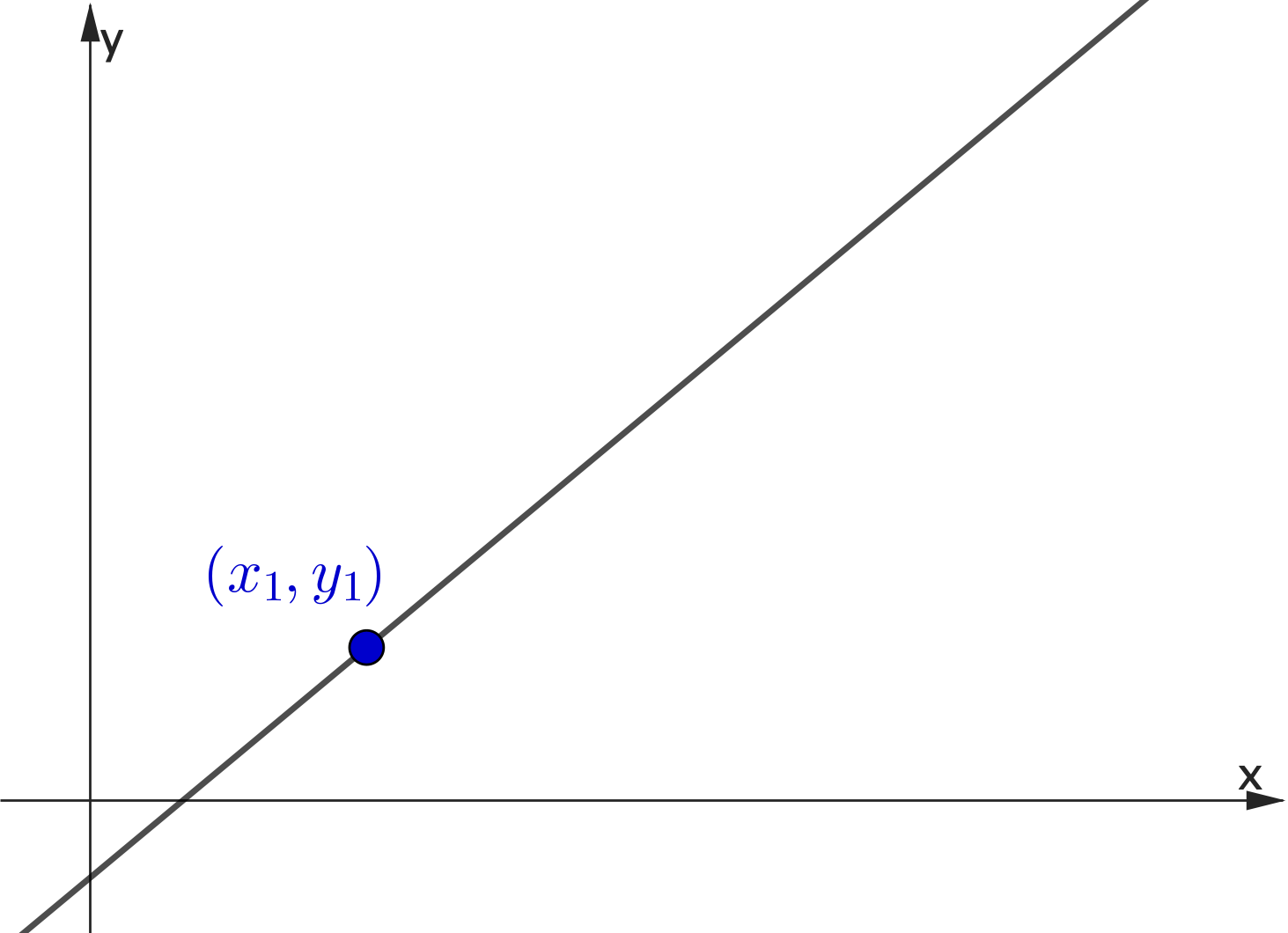
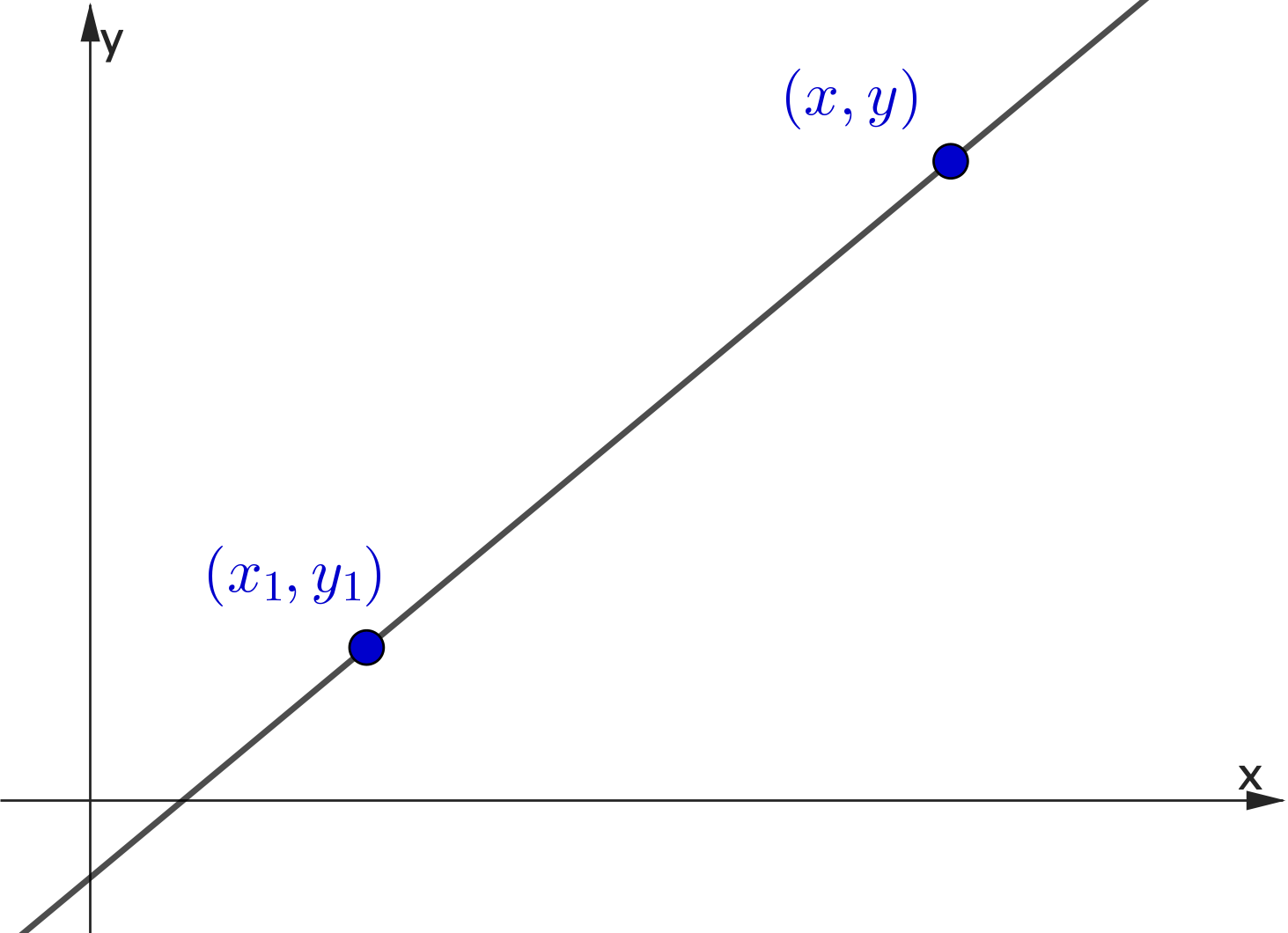
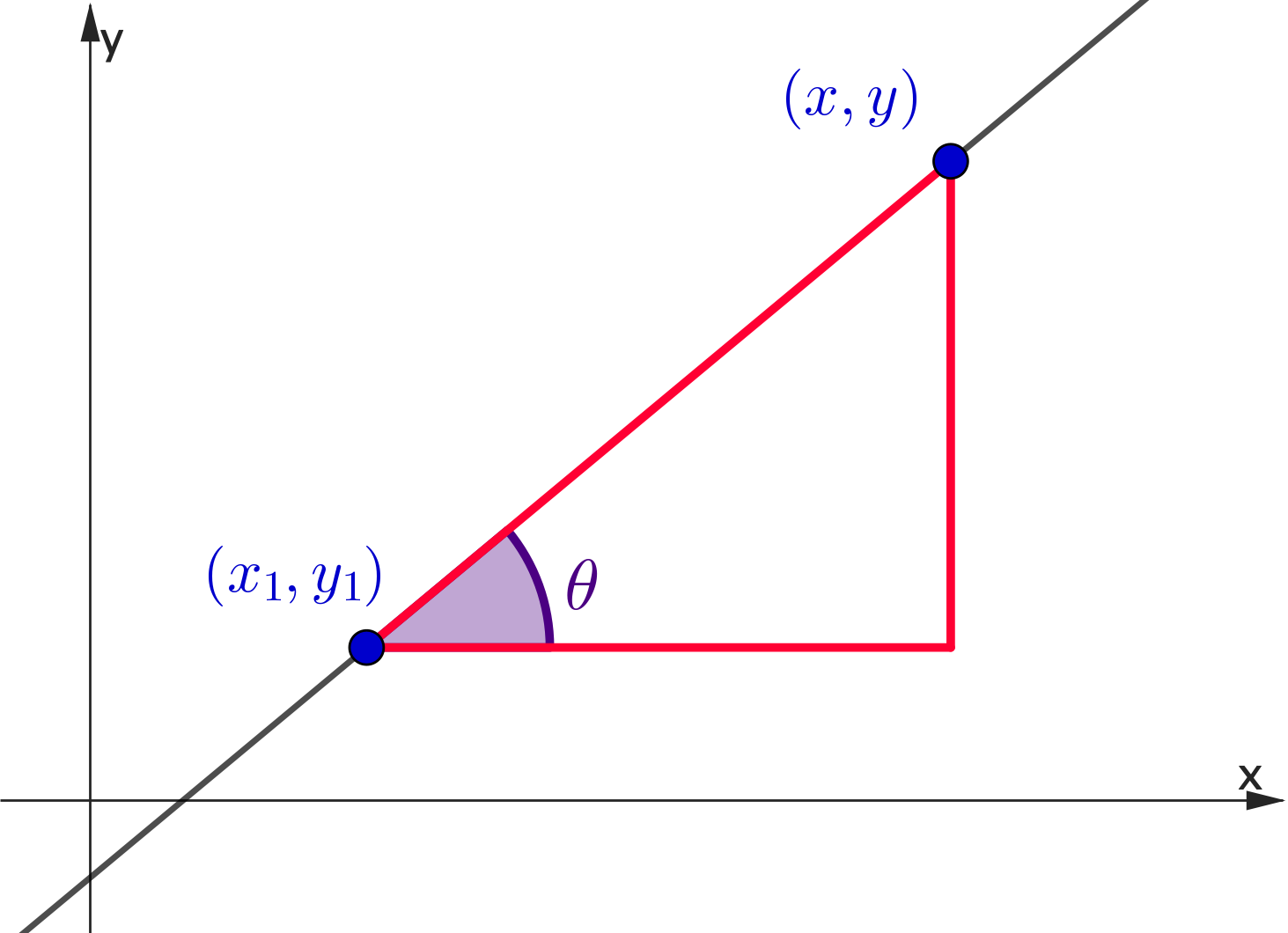
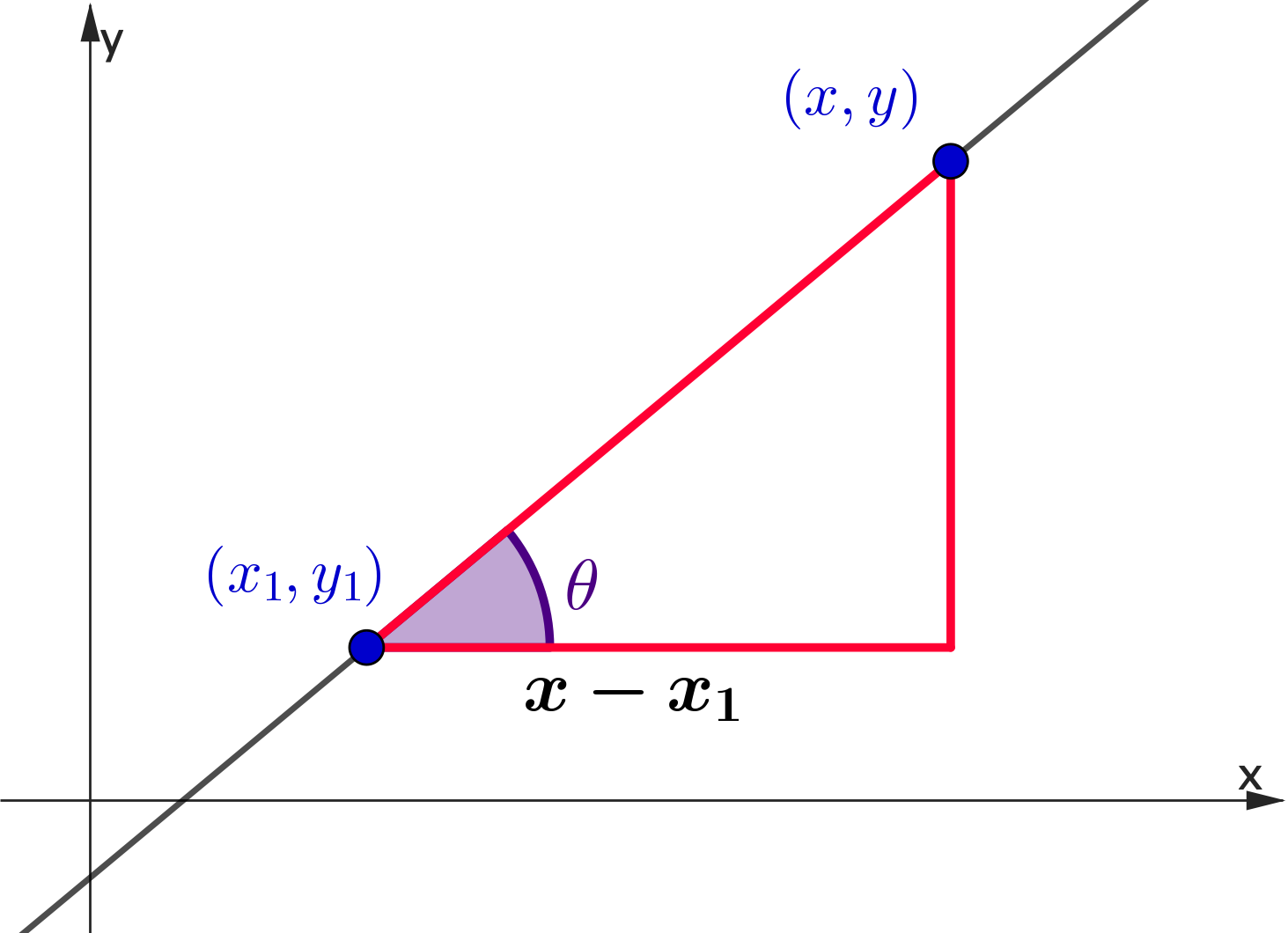
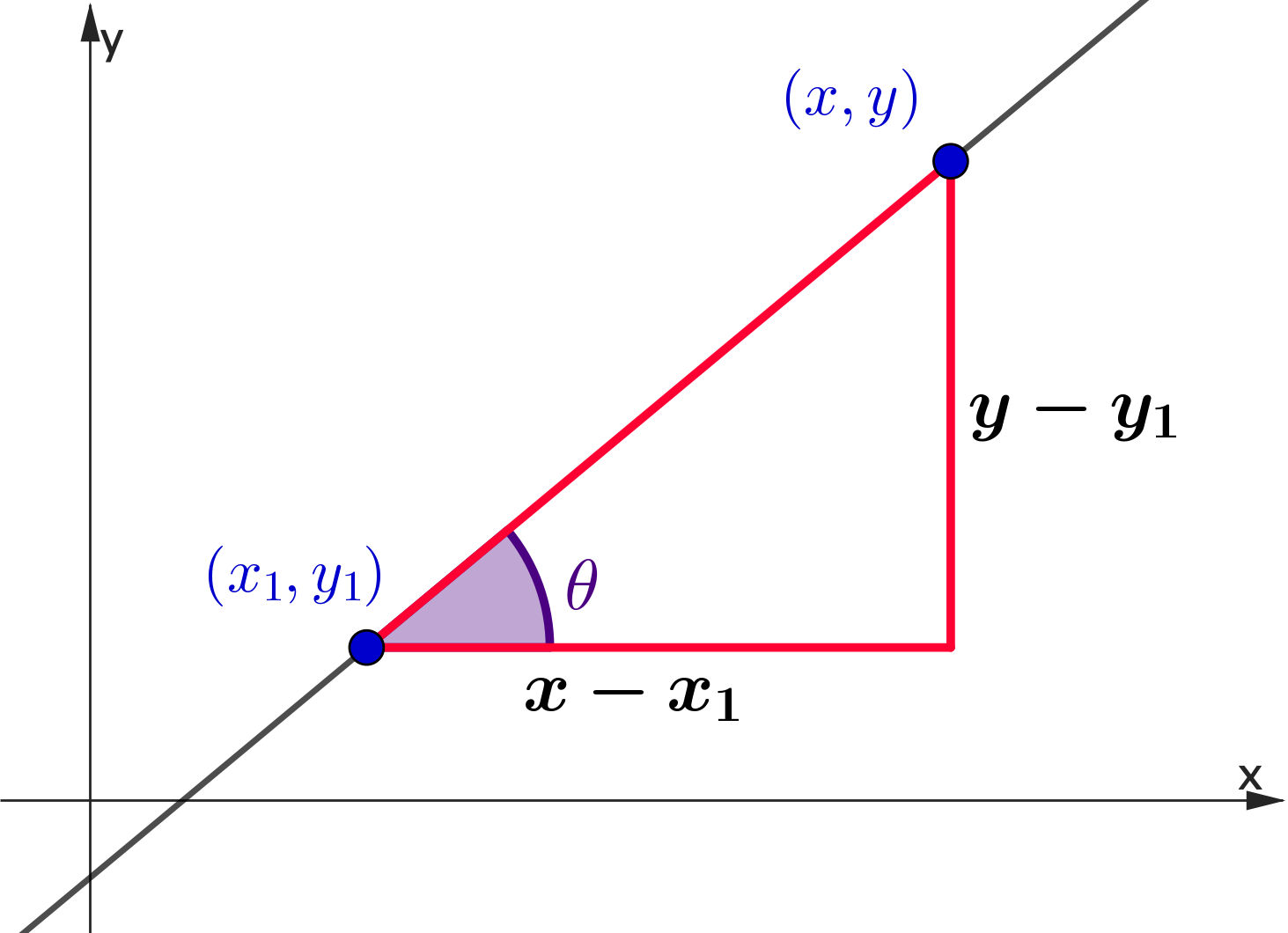
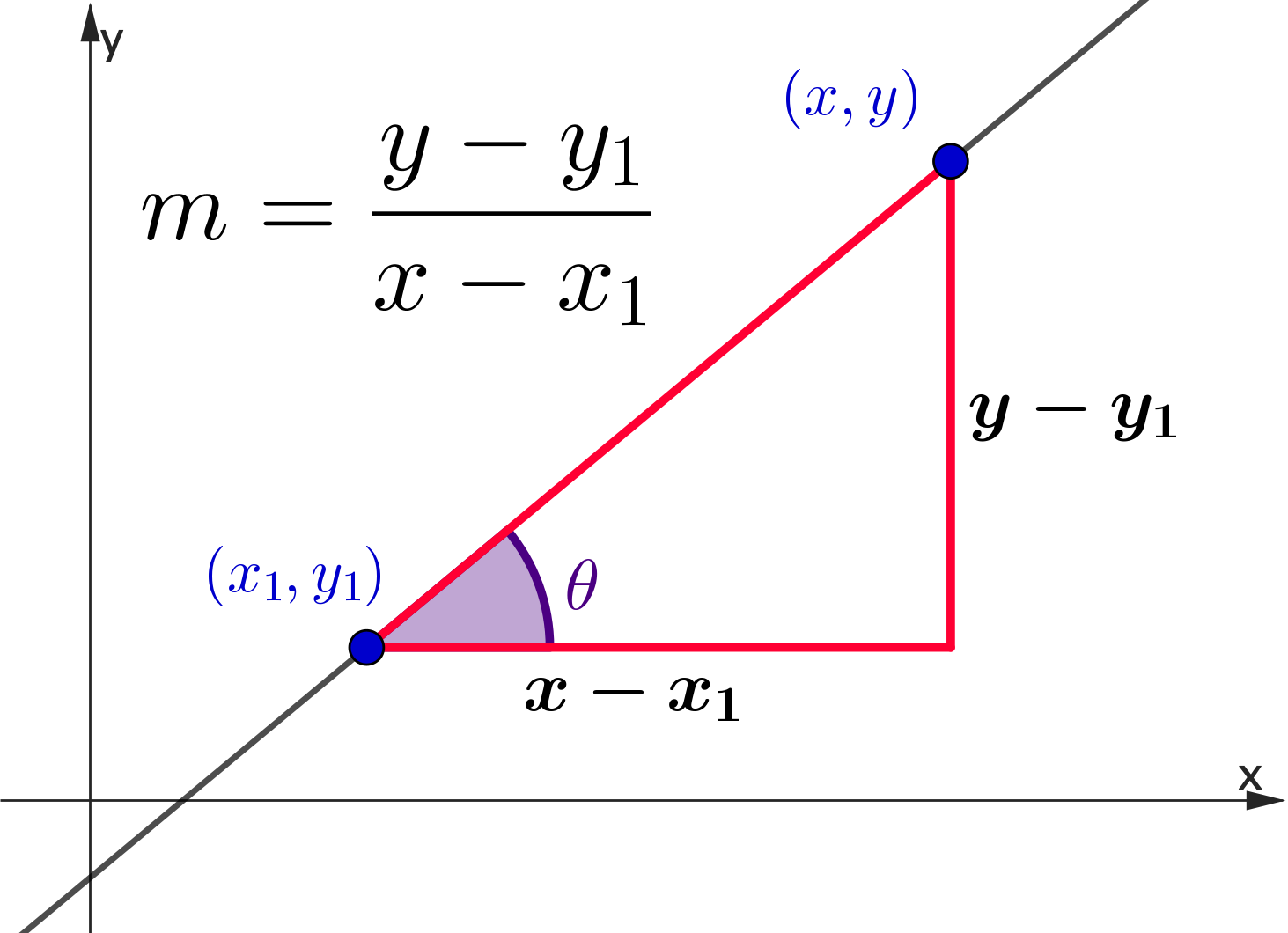
Finding the Equation of a Line
👉 $\;m = \dfrac{y-y_1}{x-x_1}\;\;$ and $\;\;m = \dfrac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}$
| $\Ra\; \dfrac{y-y_1}{x-x_1}$ | $=$ | $\dfrac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}$ |
| $\Ra\; y-y_1 $ | $=$ | $\dfrac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}\left(x-x_1\right)$ |
| $\Ra \;y-y_1 $ | $=$ | $m \left(x-x_1\right)$ |
✨ The equation of a line ✨
$y-y_1 = m \left(x-x_1\right)\;$ with $\;m = \dfrac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}$

Example 1
Find the equation of the line that has a gradient of 3 and passes through the point $(2,5).$
👉 $\;y-y_1 = m \left(x-x_1\right)$
| \(y-5\) | \(=\) | \( 3(x-2)\) |
| \(y-5\) | \(=\) | \(3x-6\) |
| \(y-5+5\) | \(=\) | \( 3x-6+5\) |
| \(y\) | \(=\) | \( 3x-1 \) |
Example 1
Find the equation of the line that has a gradient of 3 and passes through the point $(2,5).$
👉 $\;y = 3 x-1,\;$ when $\,x=2\,$ we have:
| \(y\) | \(=\) | \( 3(2)-1\) |
| \(y\) | \(=\) | \(5\;\) ✅ |

Example 2
Find the equation of the line that has a gradient of 4 and passes through the point $(-3,-7).$
👉 $\;y-y_1 = m \left(x-x_1\right)$
| \(y-(-7)\) | \(=\) | \( 4(x-(-3))\) |
| \(y+7\) | \(=\) | \(4(x+3)\) |
| \(y+7\) | \(=\) | \( 4x+12\) |
| \(y+7-7\) | \(=\) | \( 4x+12 -7 \) |
| \(y\) | \(=\) | \( 4x+5 \) |
Example 2
Find the equation of the line that has a gradient of 4 and passes through the point $(-3,-7).$
👉 $\;y = 4 x+5,\;$ when $\,x=-3\,$ we have:
| \(y\) | \(=\) | \( 4(-3)+5\) |
| \(y\) | \(=\) | \(-12+5\) |
| \(y\) | \(=\) | \(-7\;\) ✅ |

Example 3
Find the equation of the line that passes through the points
$(-2,-4)\,$ and $\,(3,11).$
👉 $\;y-y_1 = m \left(x-x_1\right),\;$ with $\;m=\dfrac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}$
| \(m\) | \(=\) | \( \dfrac{(11)-(-4)}{(3)-(-2)} \) |
| \(m\) | \(=\) | \(\dfrac{11+4}{3+2} \) |
| \(m\) | \(=\) | \(\dfrac{15}{5}\) \(\,=3\) |
Example 3
Find the equation of the line that passes through the points
$(-2,-4)\,$ and $\,(3,11).$
👉 $\;y-y_1 = m \left(x-x_1\right),\;$ with $\;m=3$
| \(y-(-4)\) | \(=\) | \( 3(x-(-2))\) |
| \(y+4\) | \(=\) | \(3(x+2)\) |
| \(y+4\) | \(=\) | \( 3x+6\) |
| \(y+4-4\) | \(=\) | \( 3x+6 -4 \) |
| \(y\) | \(=\) | \( 3x+2 \) |
Example 3
Find the equation of the line that passes through the points
$(-2,-4)\,$ and $\,(3,11).$
👉 $\;y = 3 x+2,\;$ when $\,x=-2\,$ we have:
| \(y\) | \(=\) | \( 3(-2)+2\) |
| \(y\) | \(=\) | \(-6+2\) |
| \(y\) | \(=\) | \(-4\;\) ✅ |

Two more important facts about lines!
1. Parallel lines have the same gradient
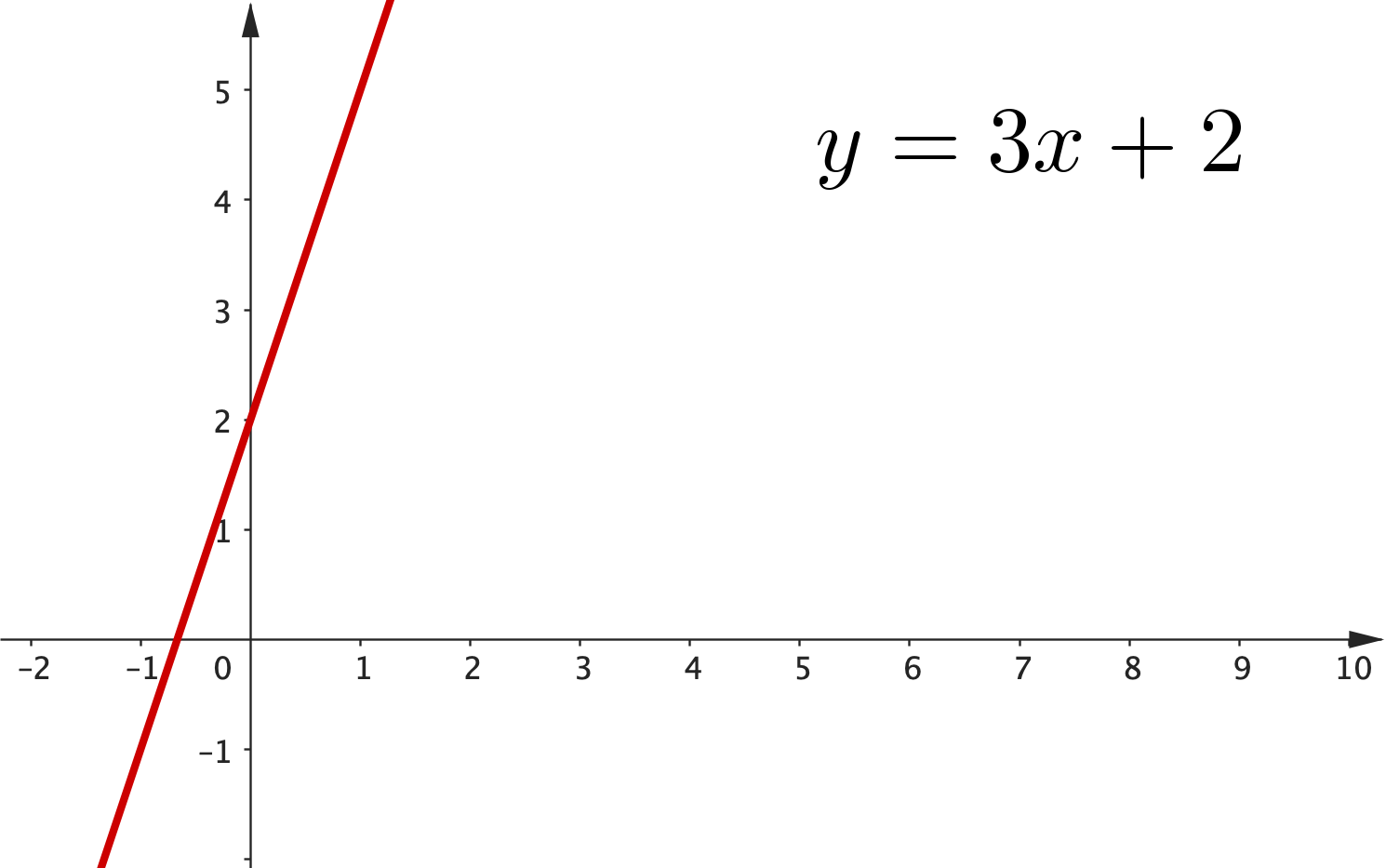
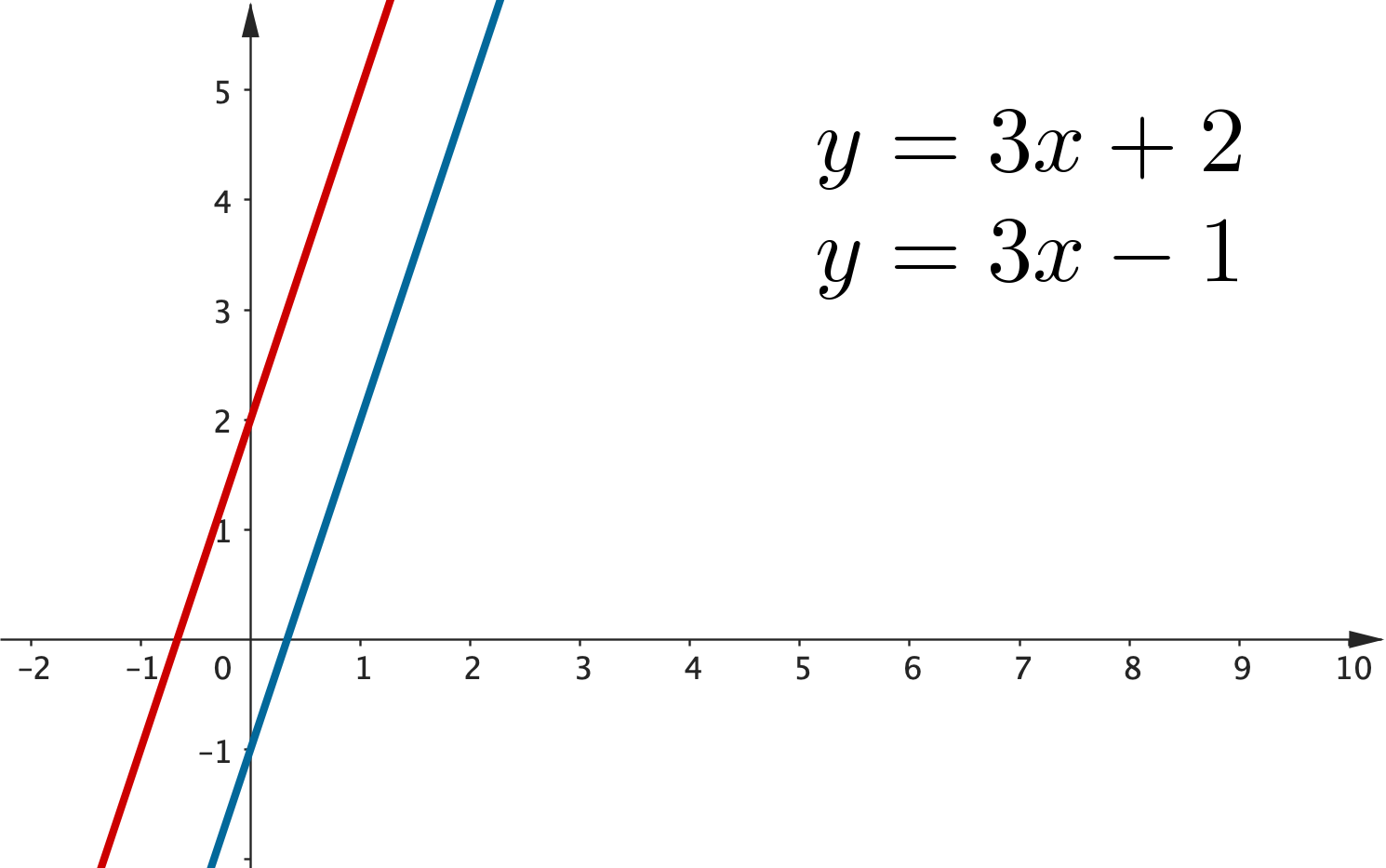
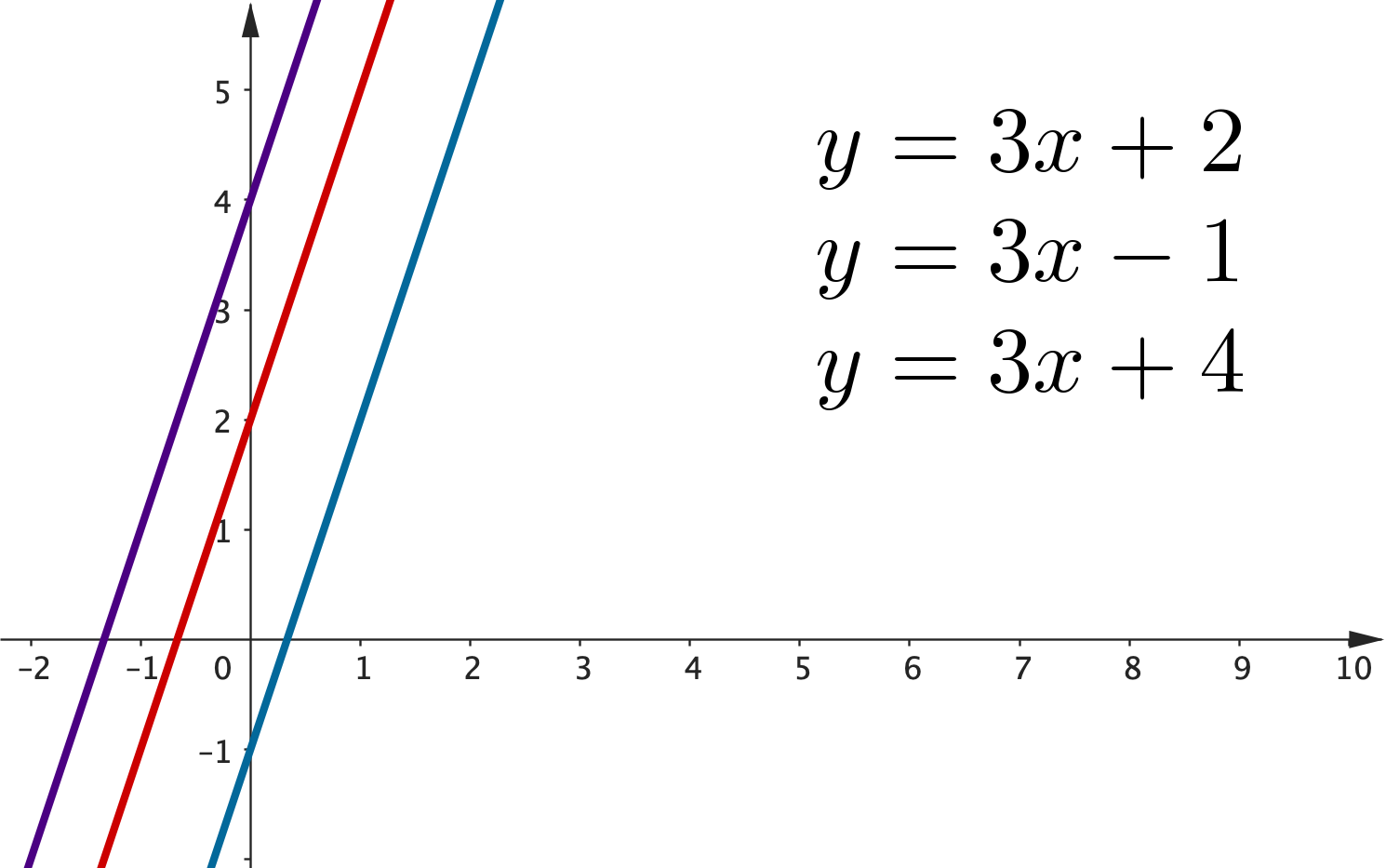
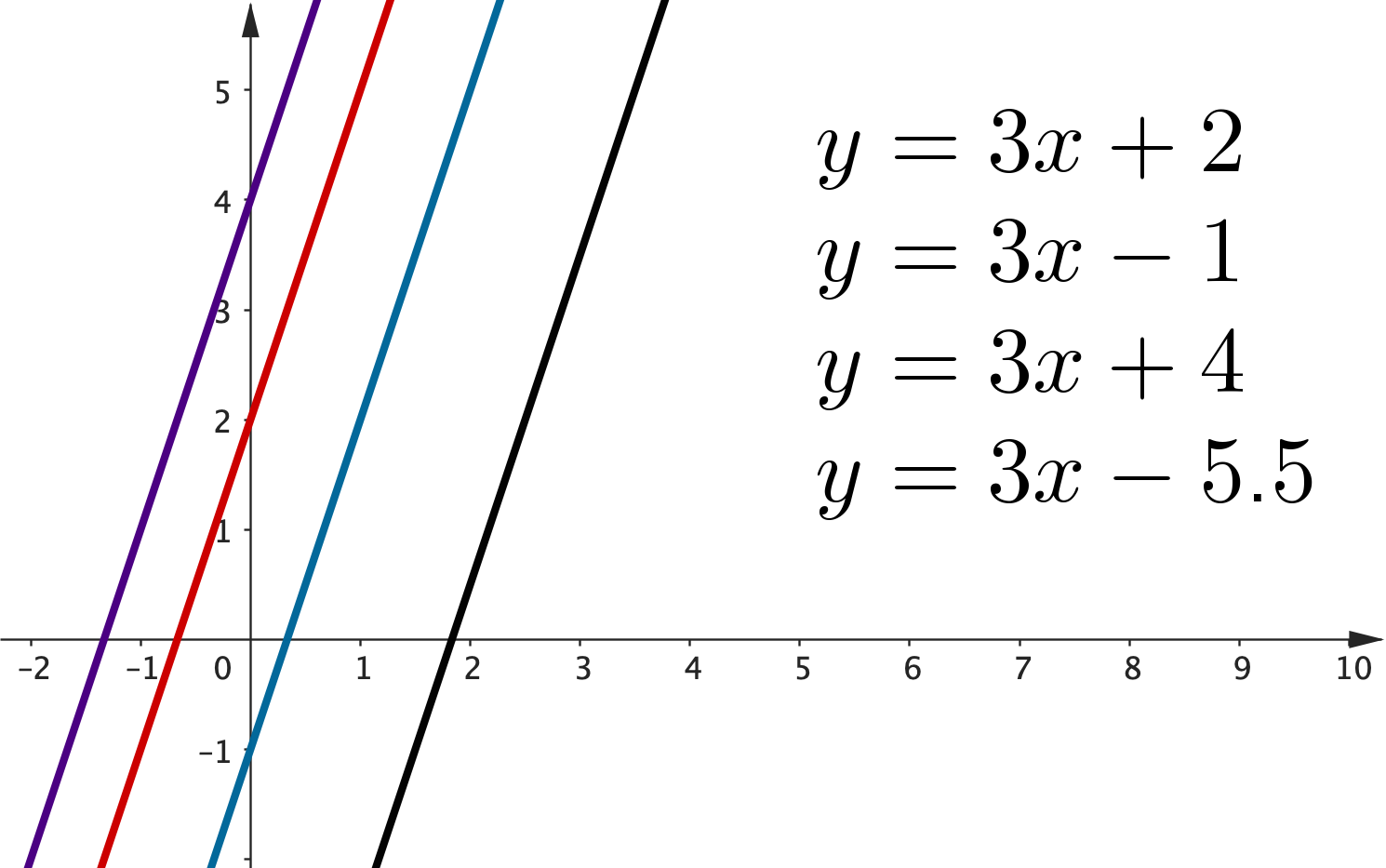
Two more important facts about lines!
2. If two lines are perpendicular, multiplying their gradients will give -1
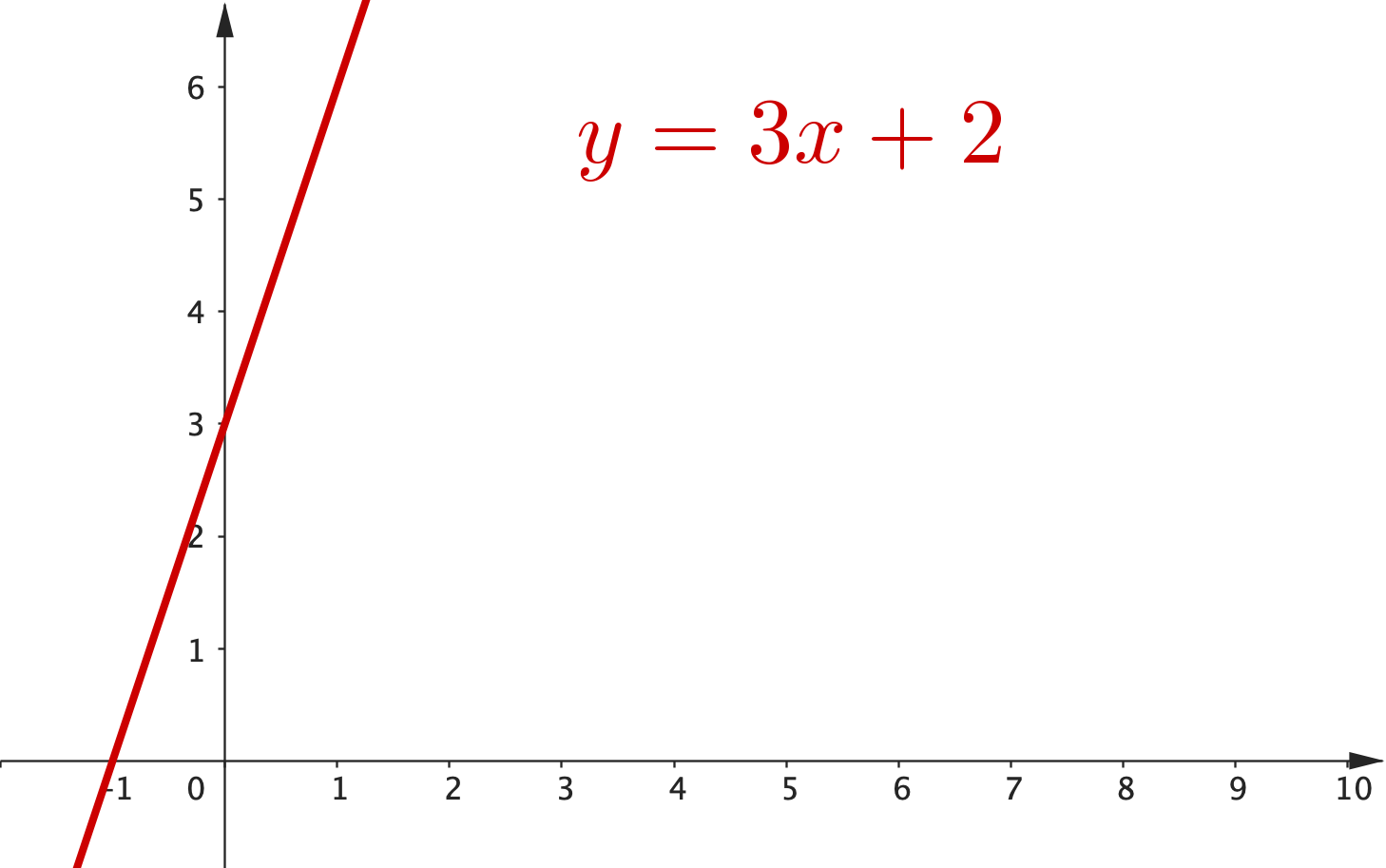
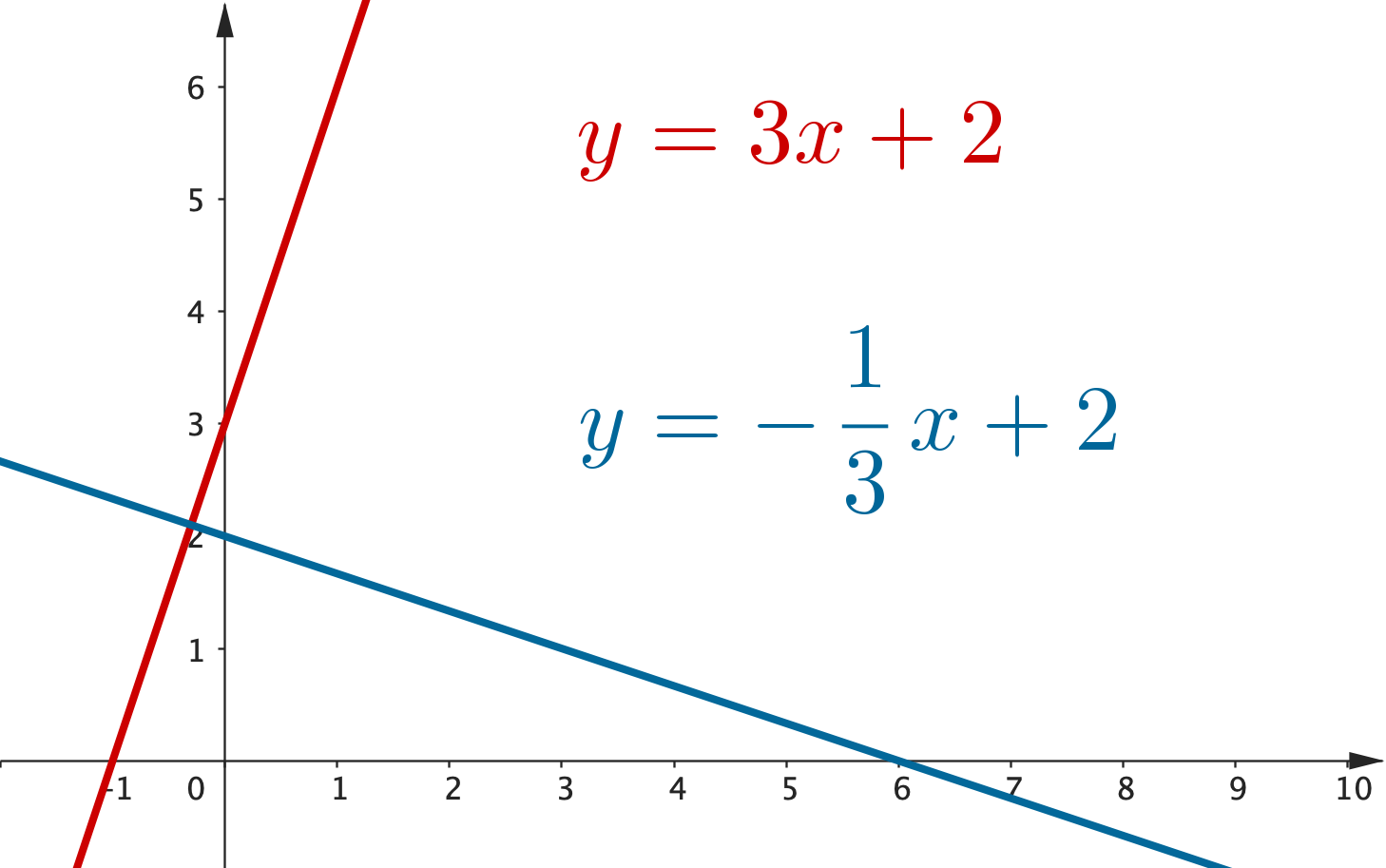
Two more important facts about lines!
• If two lines are perpendicular, multiplying their gradients will give -1
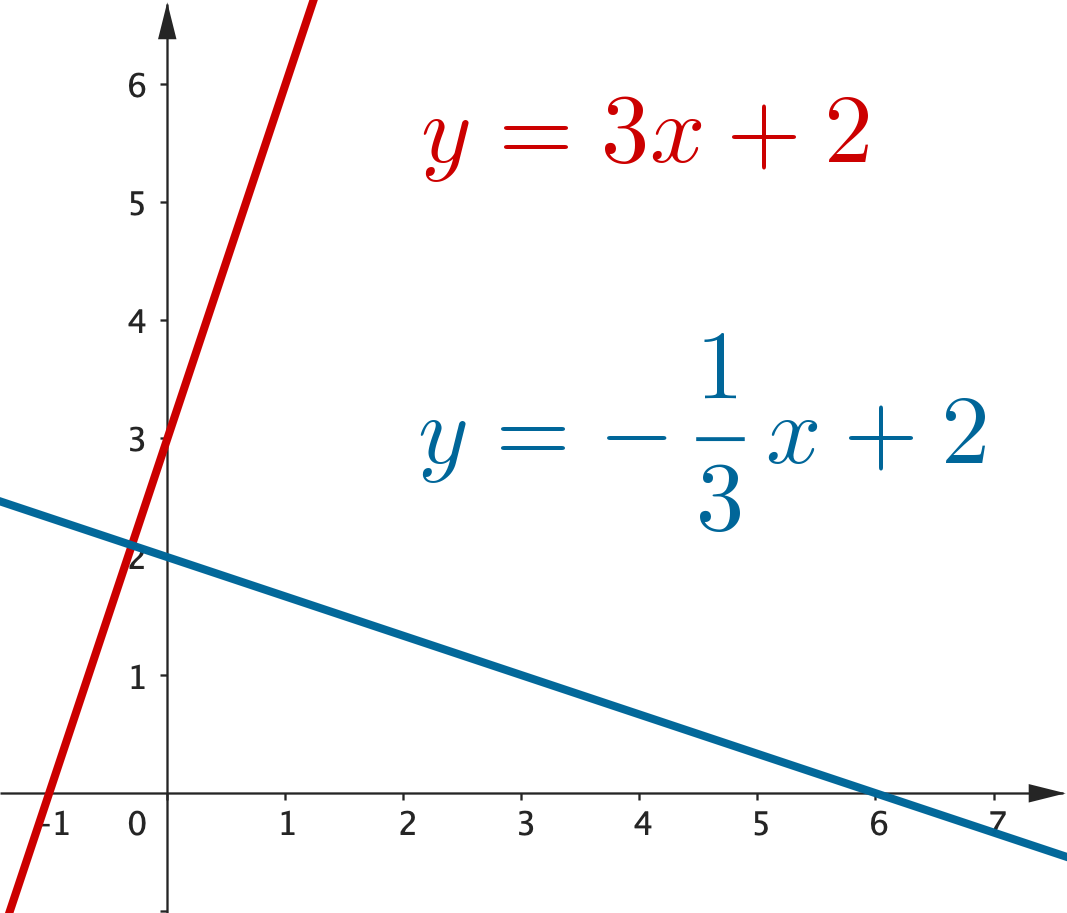
|
$m_1 = 3$ $m_2 = -\dfrac{1}{3}$ $m_1 \times m_2$ $\,= 3\times \left(-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)$ $\qquad \quad\, = -1$ |
Graphing Quadratic Equations
Graphing Quadratic Equations
Graphing Quadratic Equations
Graphing Quadratic Equations
Graphing Quadratic Equations
$y = ax^2 + bx + c\;$ where $\;a,b,c$ constants
• The $y$-intercept is $c.$
• To find $x$-intercept, let $y=0.$
• Turning point: $x=\dfrac{-b}{2a}.$
👉 $\;x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}$
Example 1
|
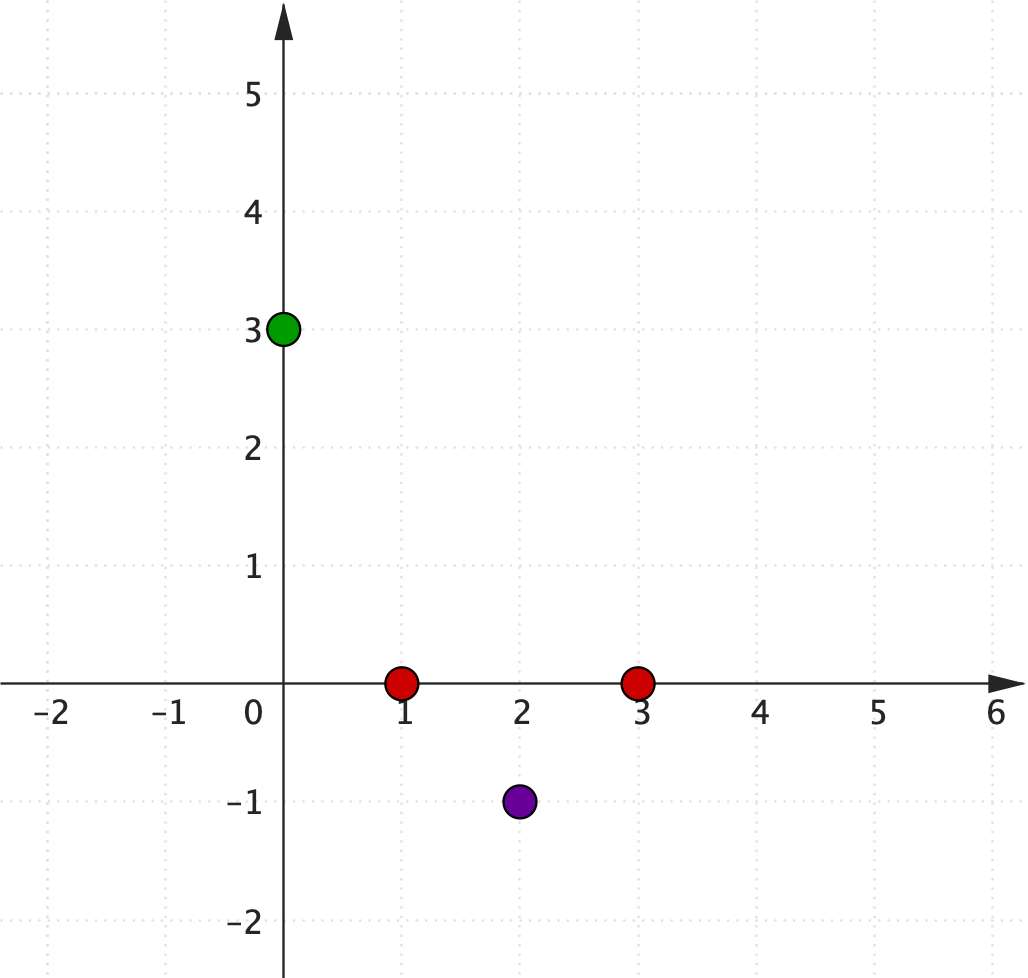
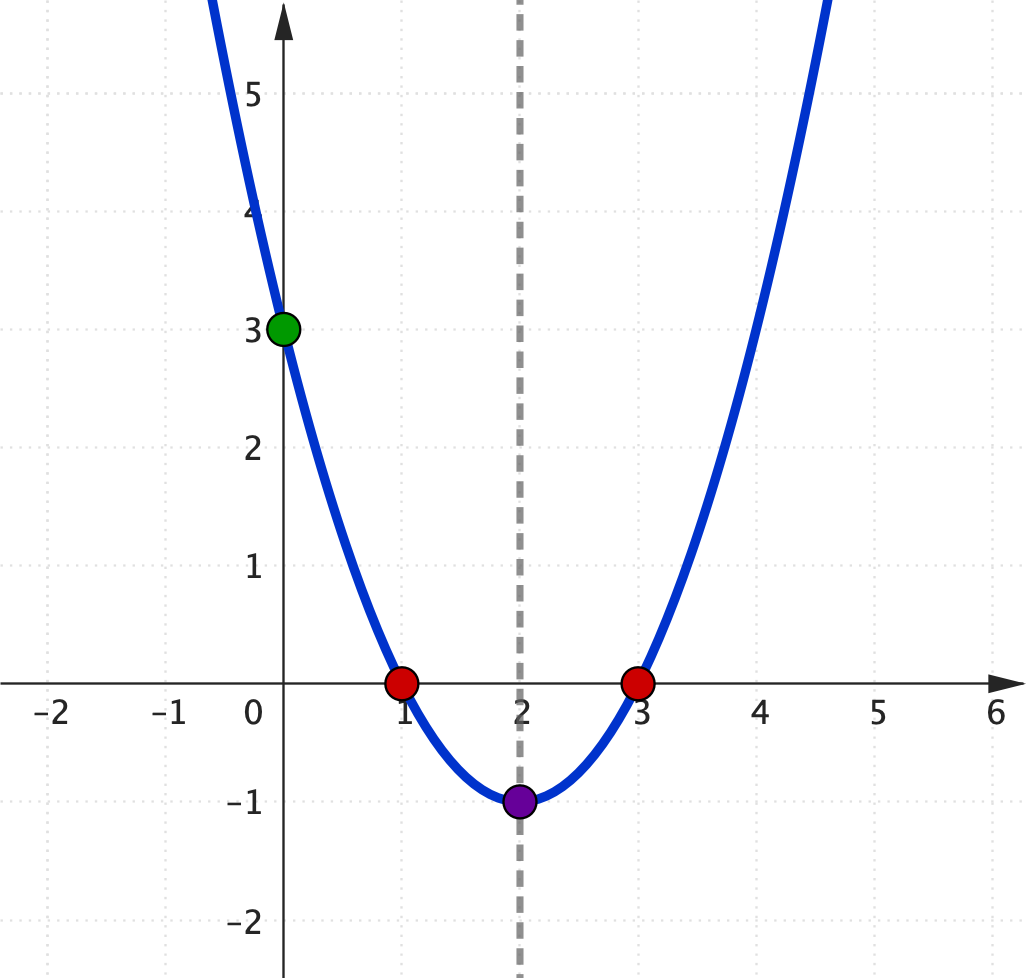
$y=x^2 - 4x + 3$ • $y$-intercept $c=3.$
• To find $x$-intercepts, $x^2 - 4x + 3=0$ $(x-1)(x-3)=0$ $x=1,\,$ $\, x= 3$ |
Example 1
|
$y=x^2 - 4x + 3$ • Turning point: $x=\dfrac{-b}{2a}$ $ = \dfrac{-(-4)}{2(1)}$ $\quad = 2$
Subs. in quadratic: $\quad = -1$ |
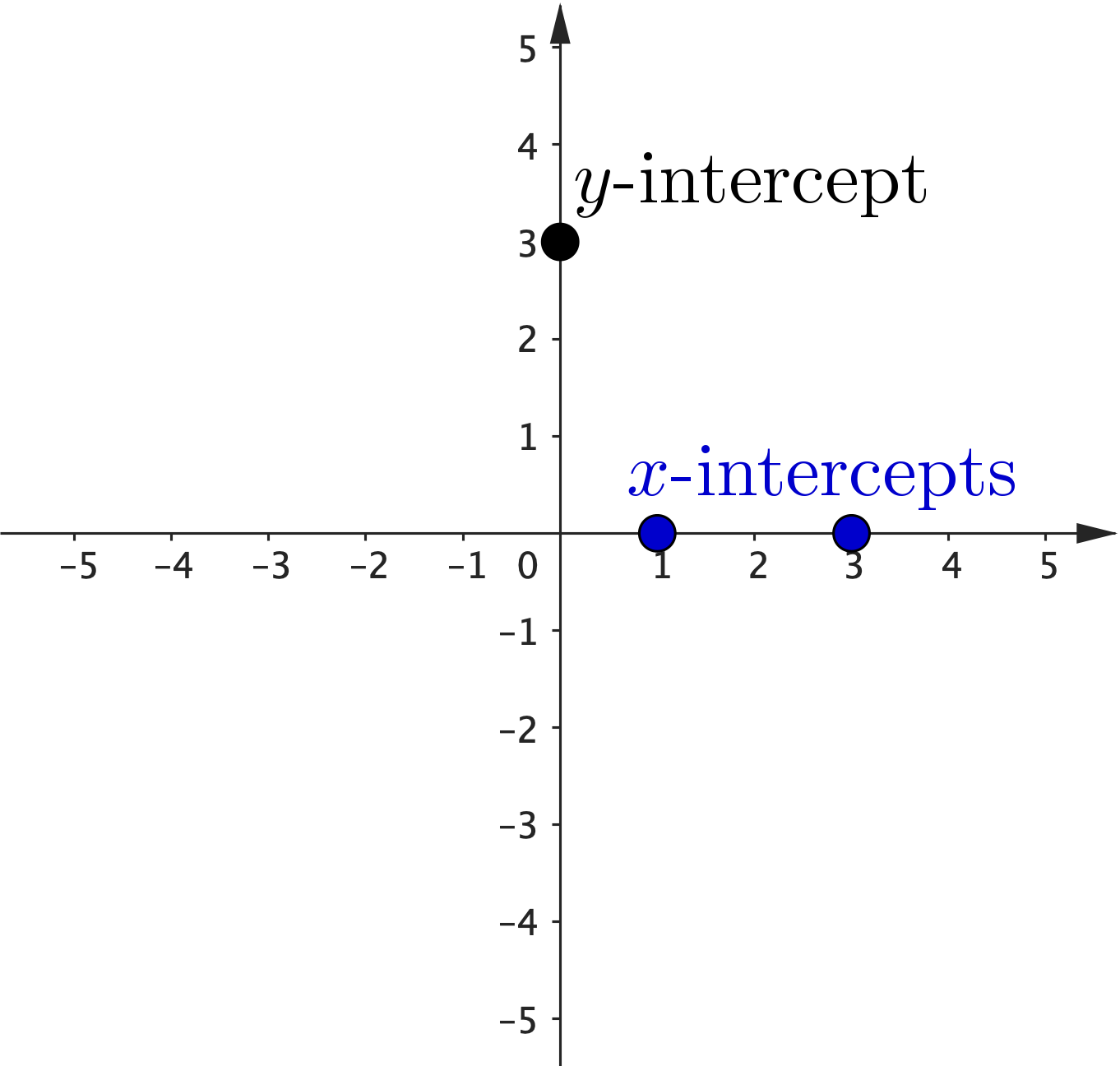
Example 1
|
• $y$-intercept: 🟢 $\,(0,3)$ • $x$-intercepts: 🔴 $\,(1,0), (3,0)$ • Turning point: 🟣 $\, (2,-1)$ |
Solving Simultaneous Equations
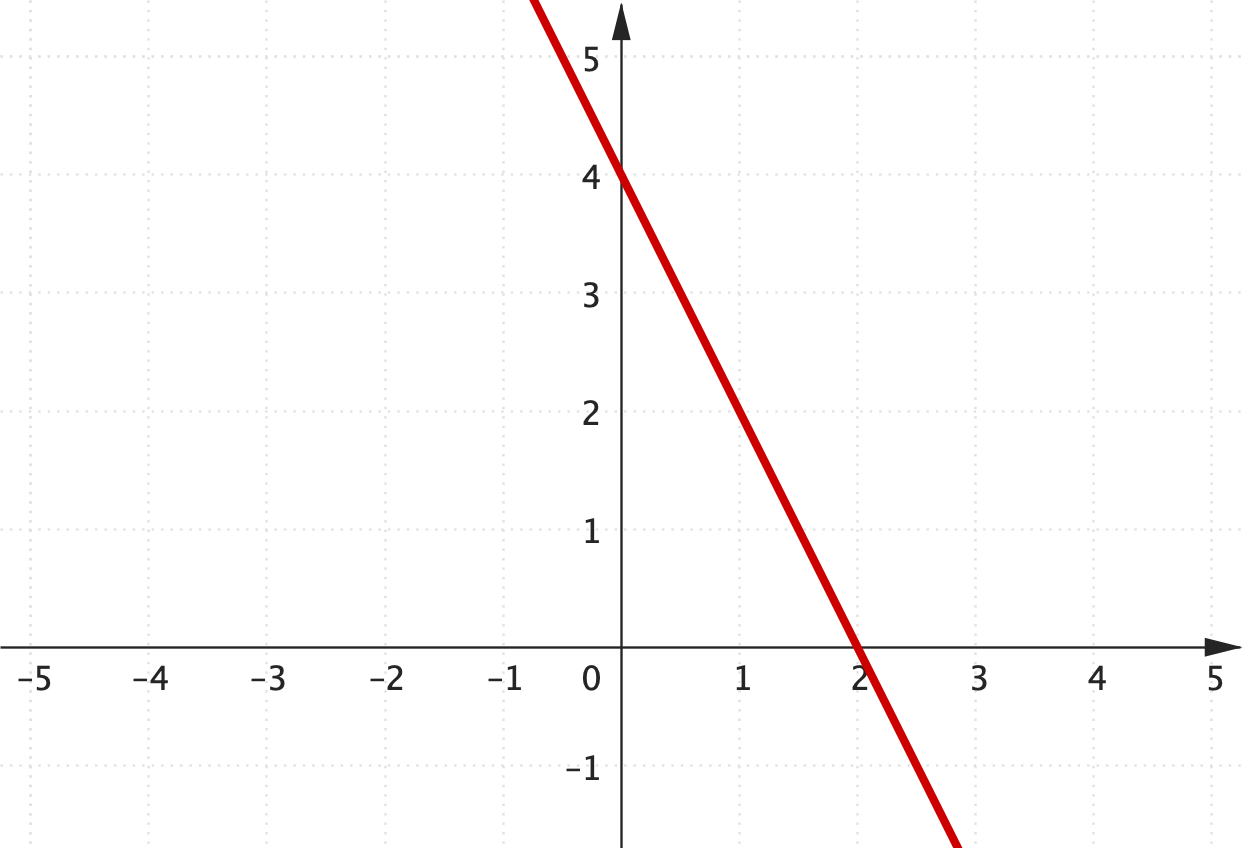
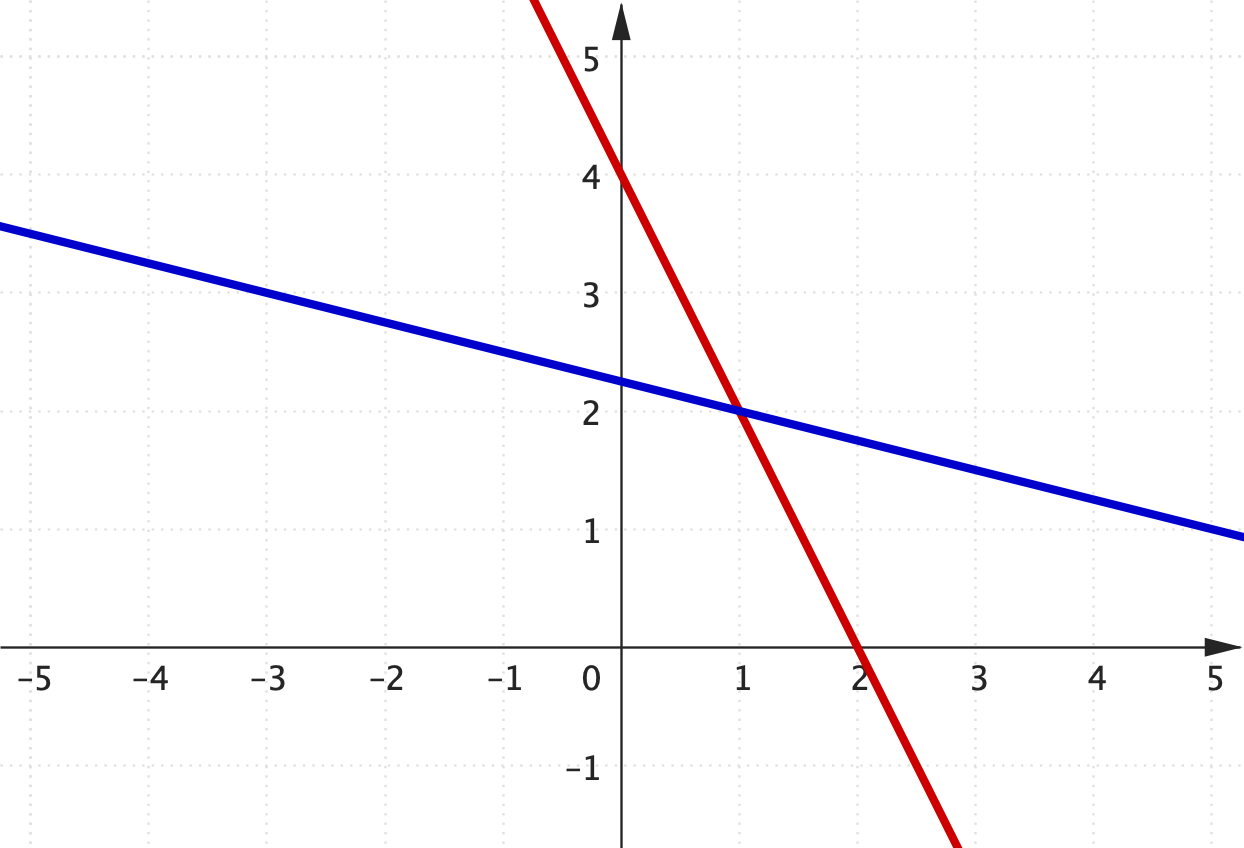
Consider
$2x+y = 4$
$x+4y = 9$
Solving Simultaneous Equations
Example 1: Consider the system of two linear equations:
$2x+y = 4$ 1
$x+4y = 9$ 2
From 2 we solve for $x$:
\( x +4y-4y= 9 + 4y - 4y \qquad \qquad \qquad\qquad \)
\( x = 9 - 4y \) \(\,=\, 9 - 4(2)\) \(\, =\, 1\)
Substitute this value in 1 to solve for $y$:
\( 2(9-4y) + y = 4 \;\) \(\;\Ra \,18 - 8y + y = 4 \)
\( 18 - 7y = 4 \;\) \(\;\Ra \, y = 2 \)
Solving Simultaneous Equations
The system of two linear equations (simultaneous equations)
$2x+y = 4$
$x+4y = 9$
has a solution: $\,x = 1\,$ and $\,y = 2.$
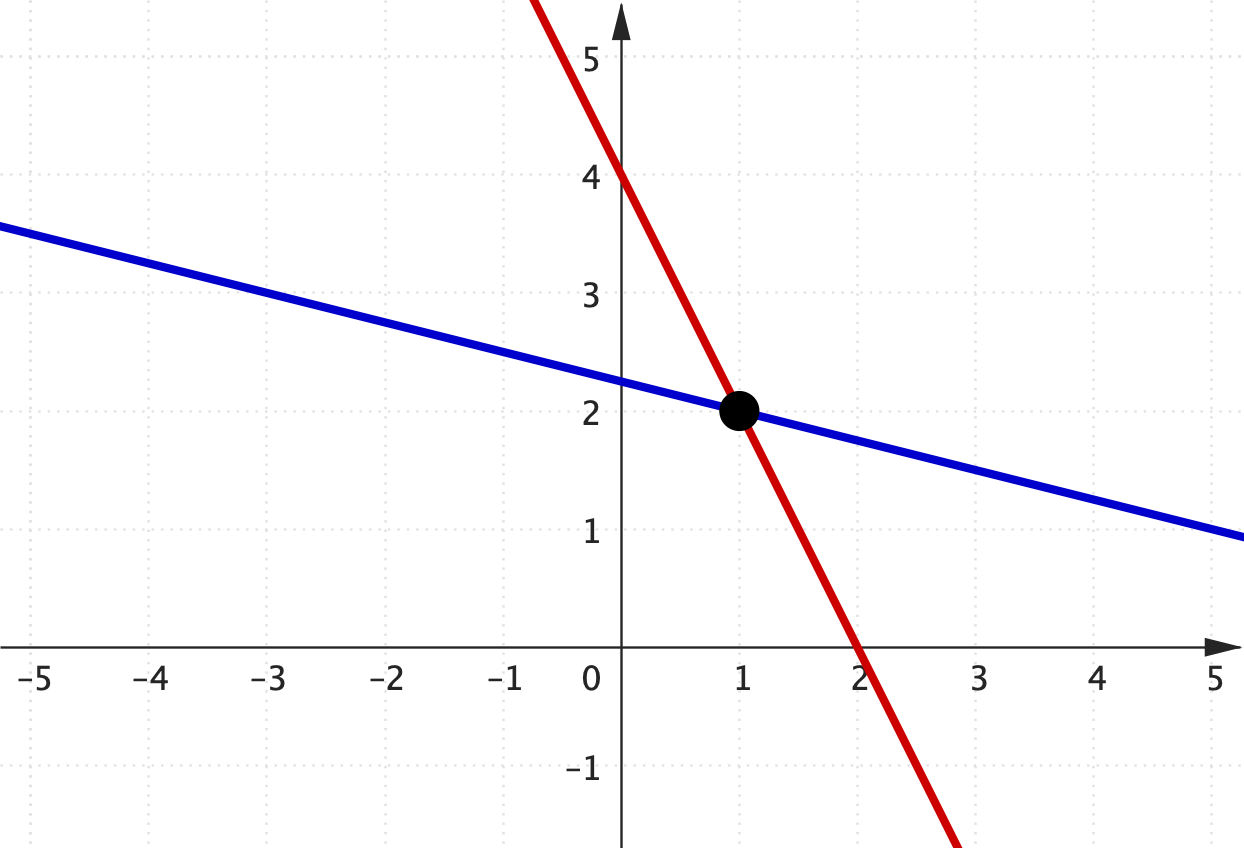
Solving Simultaneous Equations
The system of two linear equations
$2x+y = 4$
$x+4y = 9$
has a solution: $\,x = 1\,$ and $\,y = 2.$
Checking it is correct:
$2(1)+(2) = 4$ ✅
$(1)+4(2) = 9$ ✅

Final remarks: Solving Simultaneous Equations
Methods to solve simultaneous equations:
- Substitution method 👈 For Foundation Mathematics
- Elimination method 👈 Prefer for large systems
\begin{cases} 2x + 3y = 5,\\ 4x - y = 6. \end{cases}
\begin{cases} 2x_1 - x_2 + 3x_3 + x_4 + x_5 = 7,\\ - x_1 + 4x_2 - x_3 + 2x_4 - 2x_5 = -1,\\ 3x_1 + 2x_2 + 5x_3 - x_4 + x_5 = 12,\\ x_1 + x_2 - 2x_3 + 4x_4 + x_5 = 3,\\ x_1 - 3x_2 + x_3 + x_4 + 6x_5 = 8. \end{cases}
A very large system of linear equations 🤓
\[ \begin{eqnarray*} x_1 - 2x_2 + 3x_3 - 4x_4 + 5x_5 - 6x_6 + 7x_7 - 8x_8 + 9x_9 - 10x_{10} &=& 5,\\ -2x_1 + 3x_2 - 4x_3 + 5x_4 - 6x_5 + 7x_6 - 8x_7 + 9x_8 - 10x_9 + x_{10} &=& -7,\\ 3x_1 - 4x_2 + 5x_3 - 6x_4 + 7x_5 - 8x_6 + 9x_7 - 10x_8 + x_9 - 2x_{10} &=& 8,\\ -4x_1 + 5x_2 - 6x_3 + 7x_4 - 8x_5 + 9x_6 - 10x_7 + x_8 - 2x_9 + 3x_{10} &=& -3,\\ 5x_1 - 6x_2 + 7x_3 - 8x_4 + 9x_5 - 10x_6 + x_7 - 2x_8 + 3x_9 - 4x_{10} &=& 12,\\ -6x_1 + 7x_2 - 8x_3 + 9x_4 - 10x_5 + x_6 - 2x_7 + 3x_8 - 4x_9 + 5x_{10} &=& -9,\\ 7x_1 - 8x_2 + 9x_3 - 10x_4 + x_5 - 2x_6 + 3x_7 - 4x_8 + 5x_9 - 6x_{10} &=& 14,\\ -8x_1 + 9x_2 - 10x_3 + x_4 - 2x_5 + 3x_6 - 4x_7 + 5x_8 - 6x_9 + 7x_{10} &=& -11,\\ 9x_1 - 10x_2 + x_3 - 2x_4 + 3x_5 - 4x_6 + 5x_7 - 6x_8 + 7x_9 - 8x_{10} &=& 16,\\ -10x_1 + x_2 - 2x_3 + 3x_4 - 4x_5 + 5x_6 - 6x_7 + 7x_8 - 8x_9 + 9x_{10} &=& -13 \end{eqnarray*} \]
A very large system of linear equations 🤓
\[ \begin{eqnarray*} x_1 - 2x_2 + 3x_3 - 4x_4 + 5x_5 - 6x_6 + 7x_7 - 8x_8 + 9x_9 - 10x_{10} &=& 5,\\ -2x_1 + 3x_2 - 4x_3 + 5x_4 - 6x_5 + 7x_6 - 8x_7 + 9x_8 - 10x_9 + x_{10} &=& -7,\\ 3x_1 - 4x_2 + 5x_3 - 6x_4 + 7x_5 - 8x_6 + 9x_7 - 10x_8 + x_9 - 2x_{10} &=& 8,\\ -4x_1 + 5x_2 - 6x_3 + 7x_4 - 8x_5 + 9x_6 - 10x_7 + x_8 - 2x_9 + 3x_{10} &=& -3,\\ 5x_1 - 6x_2 + 7x_3 - 8x_4 + 9x_5 - 10x_6 + x_7 - 2x_8 + 3x_9 - 4x_{10} &=& 12,\\ -6x_1 + 7x_2 - 8x_3 + 9x_4 - 10x_5 + x_6 - 2x_7 + 3x_8 - 4x_9 + 5x_{10} &=& -9,\\ 7x_1 - 8x_2 + 9x_3 - 10x_4 + x_5 - 2x_6 + 3x_7 - 4x_8 + 5x_9 - 6x_{10} &=& 14,\\ -8x_1 + 9x_2 - 10x_3 + x_4 - 2x_5 + 3x_6 - 4x_7 + 5x_8 - 6x_9 + 7x_{10} &=& -11,\\ 9x_1 - 10x_2 + x_3 - 2x_4 + 3x_5 - 4x_6 + 5x_7 - 6x_8 + 7x_9 - 8x_{10} &=& 16,\\ -10x_1 + x_2 - 2x_3 + 3x_4 - 4x_5 + 5x_6 - 6x_7 + 7x_8 - 8x_9 + 9x_{10} &=& -13 \end{eqnarray*} \]
|
👉 Linear Algebra with the help of 💻 |

|