
Foundation Mathematics
1017SCG
Week 9
Topics for Week 9
- Graphing trigonometric functions (sin and cos)
- Introduction to limits
- Evaluating limits analytically
- Continuity of functions
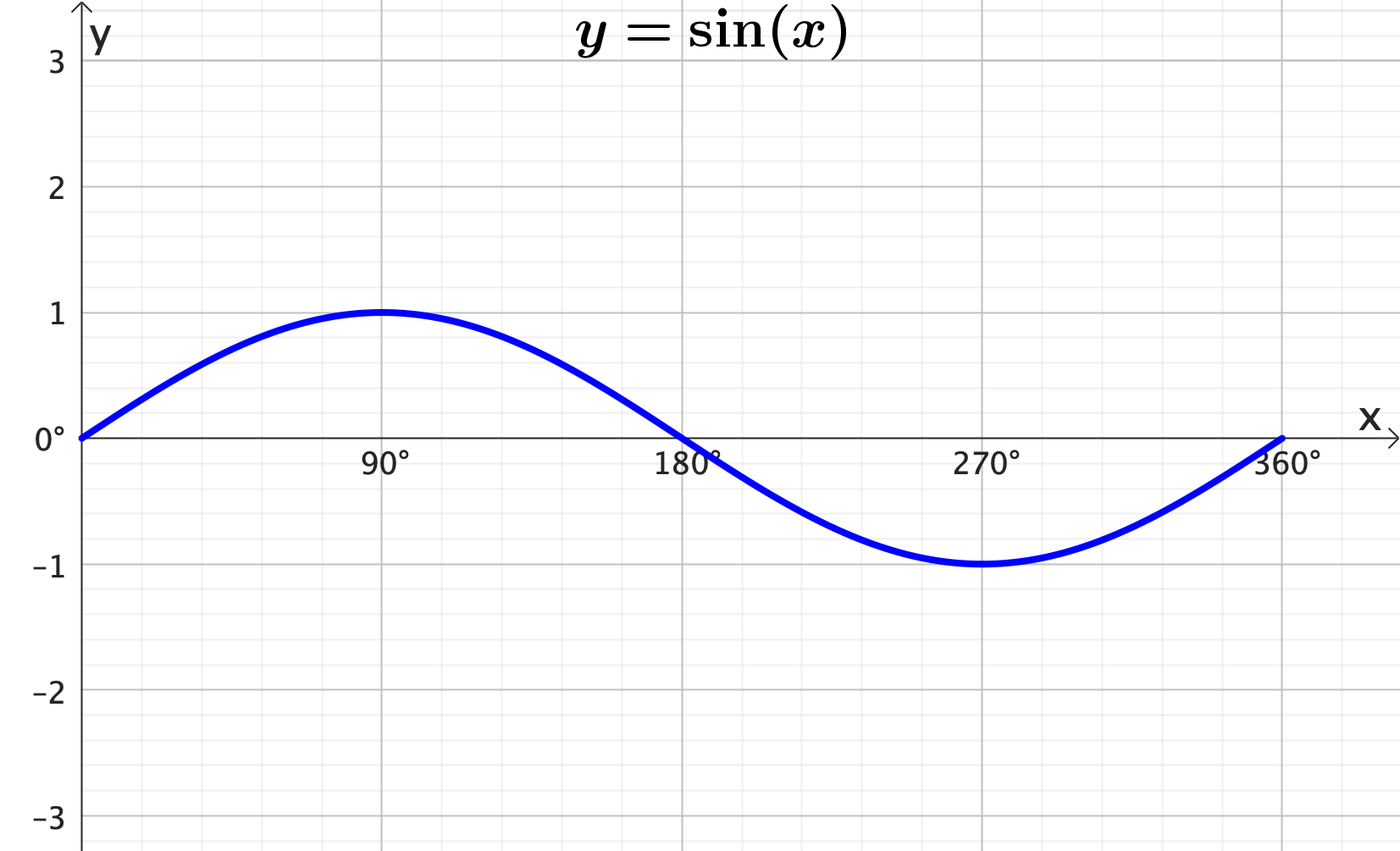
Graphing trigonometric functions (sin)
Graphing trigonometric functions (sin)
| θ | 30° | 60° | 90° | 120° | 150° | 180° | 210° | 240° | 270° | 300° | 330° | 360° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $\sin \theta$ | $1/2$ | $\sqrt{3}/2$ | $1$ | $\sqrt{3}/2$ | $1/2$ | $0$ | $-1/2$ | $-\sqrt{3}/2$ | $-1$ | $-\sqrt{3}/2$ | $-1/2$ | $0$ |
Graphing trigonometric functions (sin)
Graphing trigonometric functions (sin)
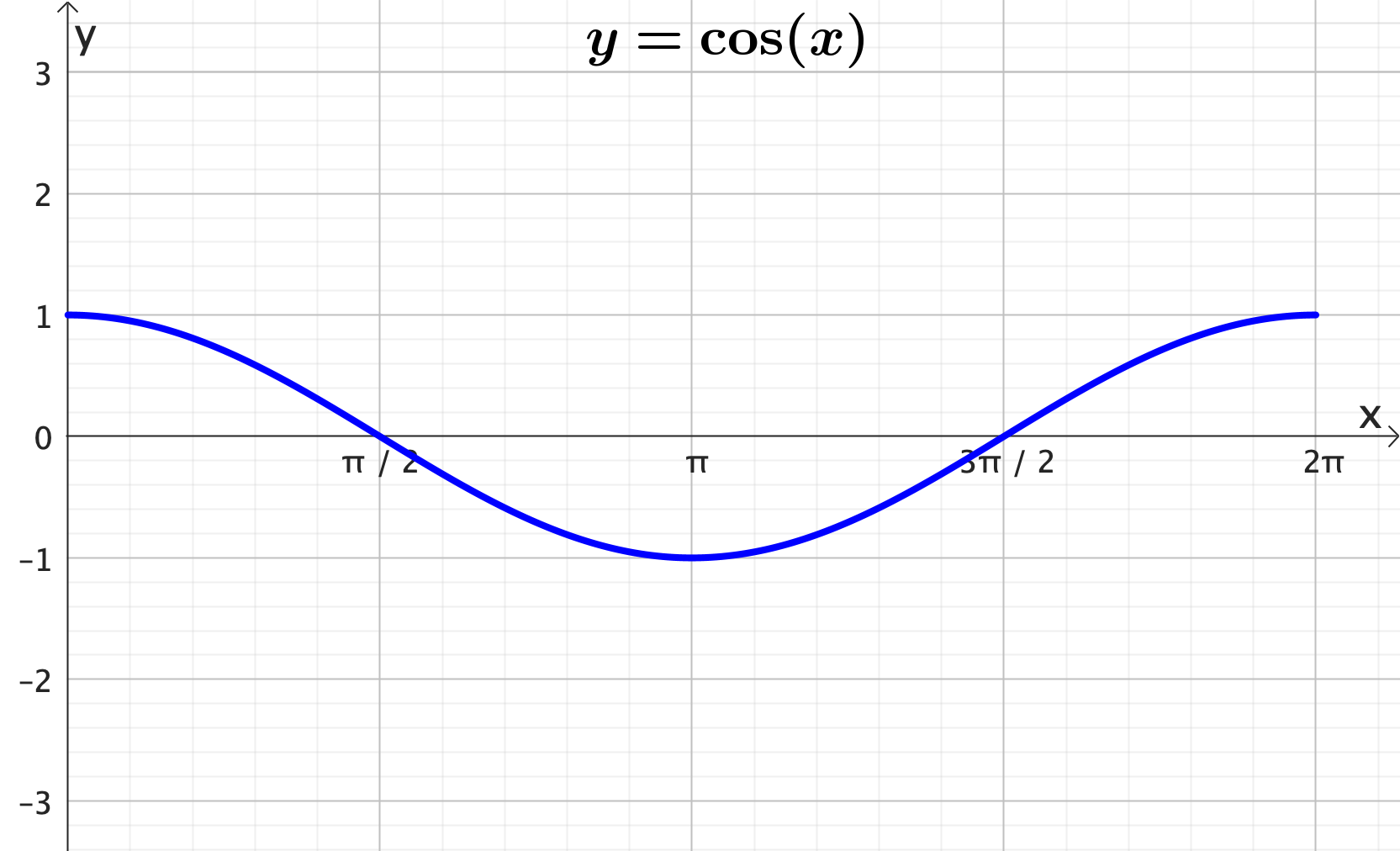
Graphing trigonometric functions (cos)
Graphing trigonometric functions (cos)

| θ | 30° | 60° | 90° | 120° | 150° | 180° | 210° | 240° | 270° | 300° | 330° | 360° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $\cos \theta$ |
Graphing trigonometric functions (cos)
Graphing trigonometric functions (cos)
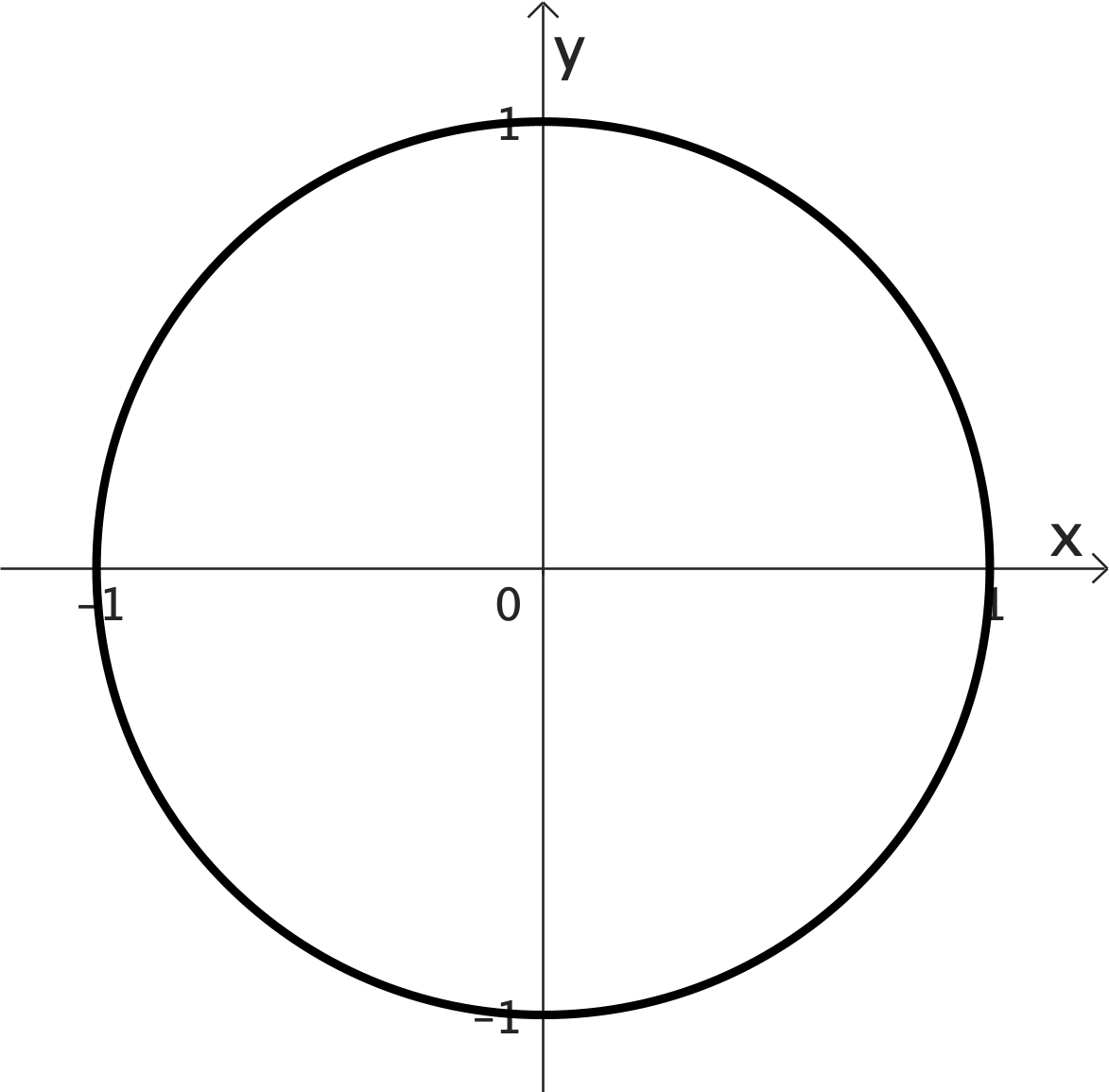
The unit circle and it's relationship with sin and cos
Graphing trigonometric functions (sin & cos in degrees)
Graphing trigonometric functions (sin & cos in radians)
The unit circle and Trigonometric functions
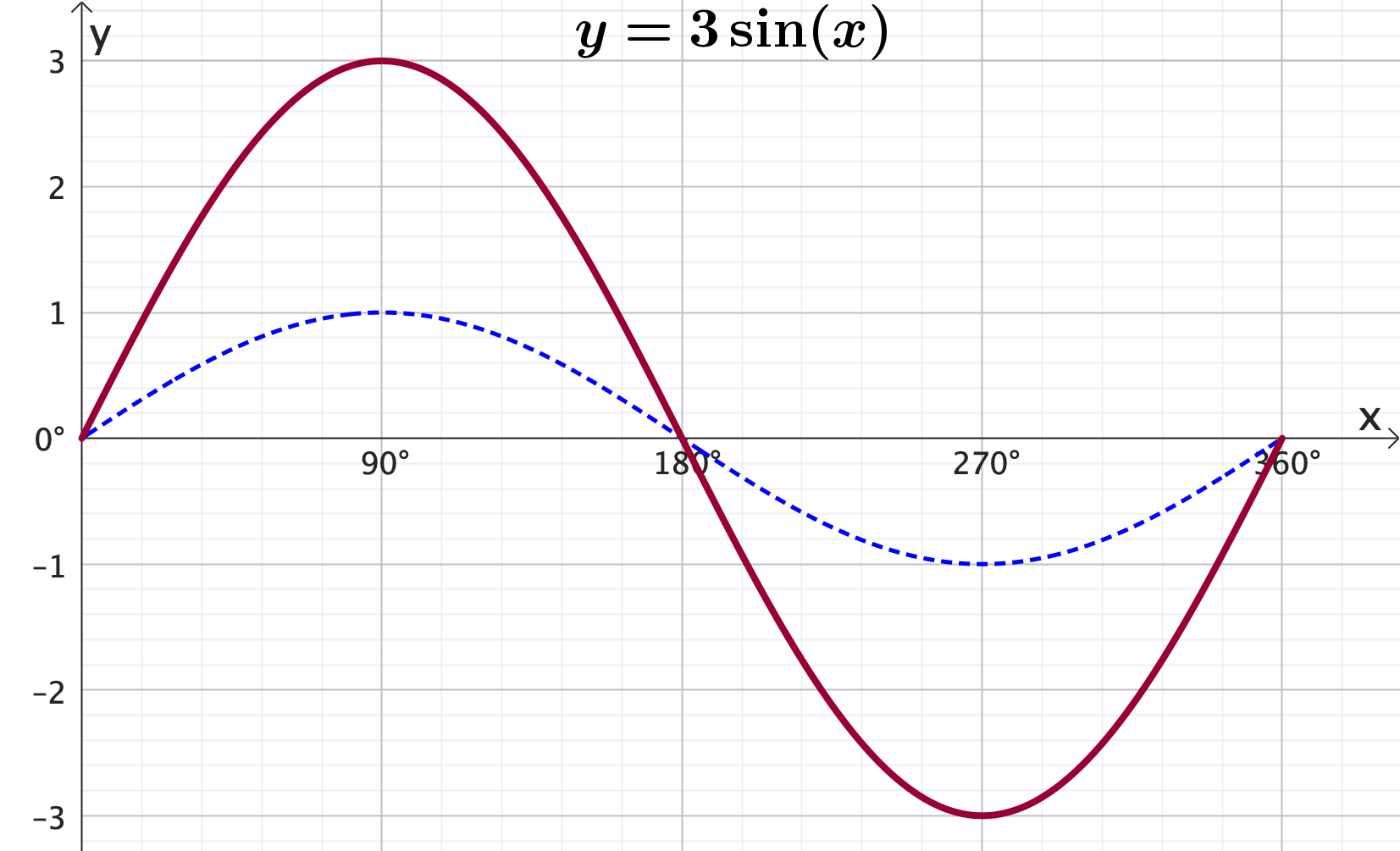
Graphing trigonometric functions: Amplitude
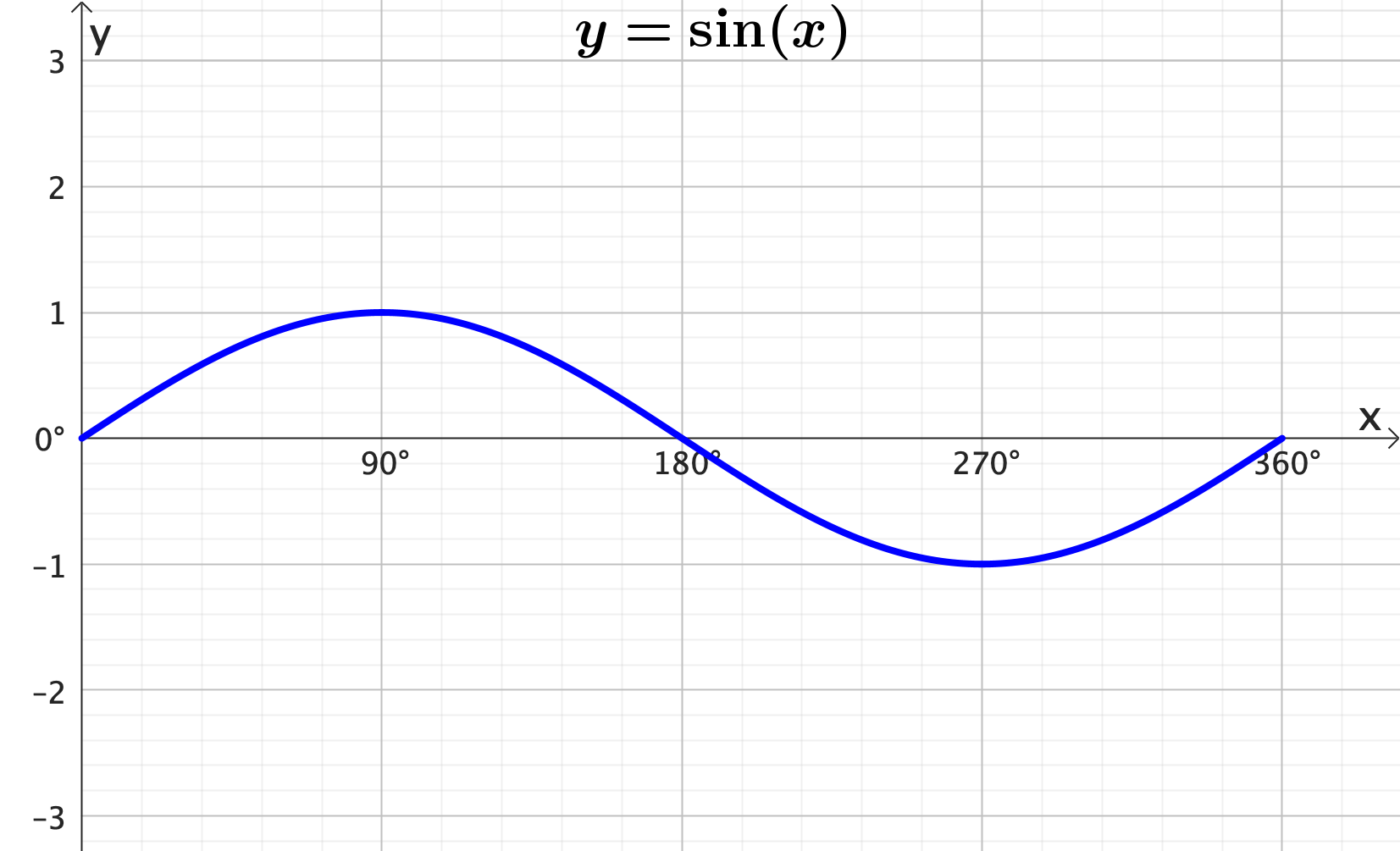
Graphing trigonometric functions: Amplitude
Graphing trigonometric functions: Frequency
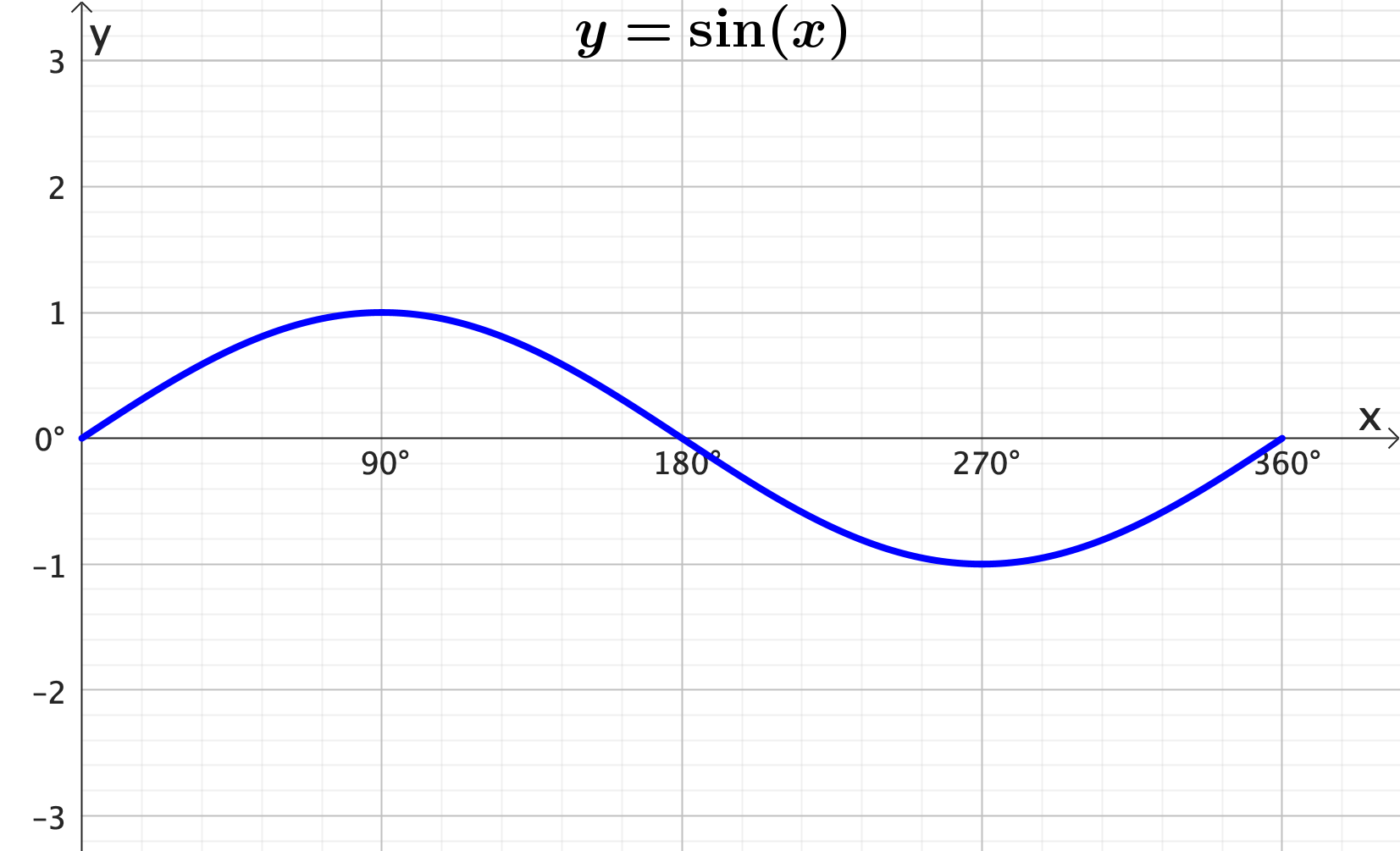
Graphing trigonometric functions: Frequency
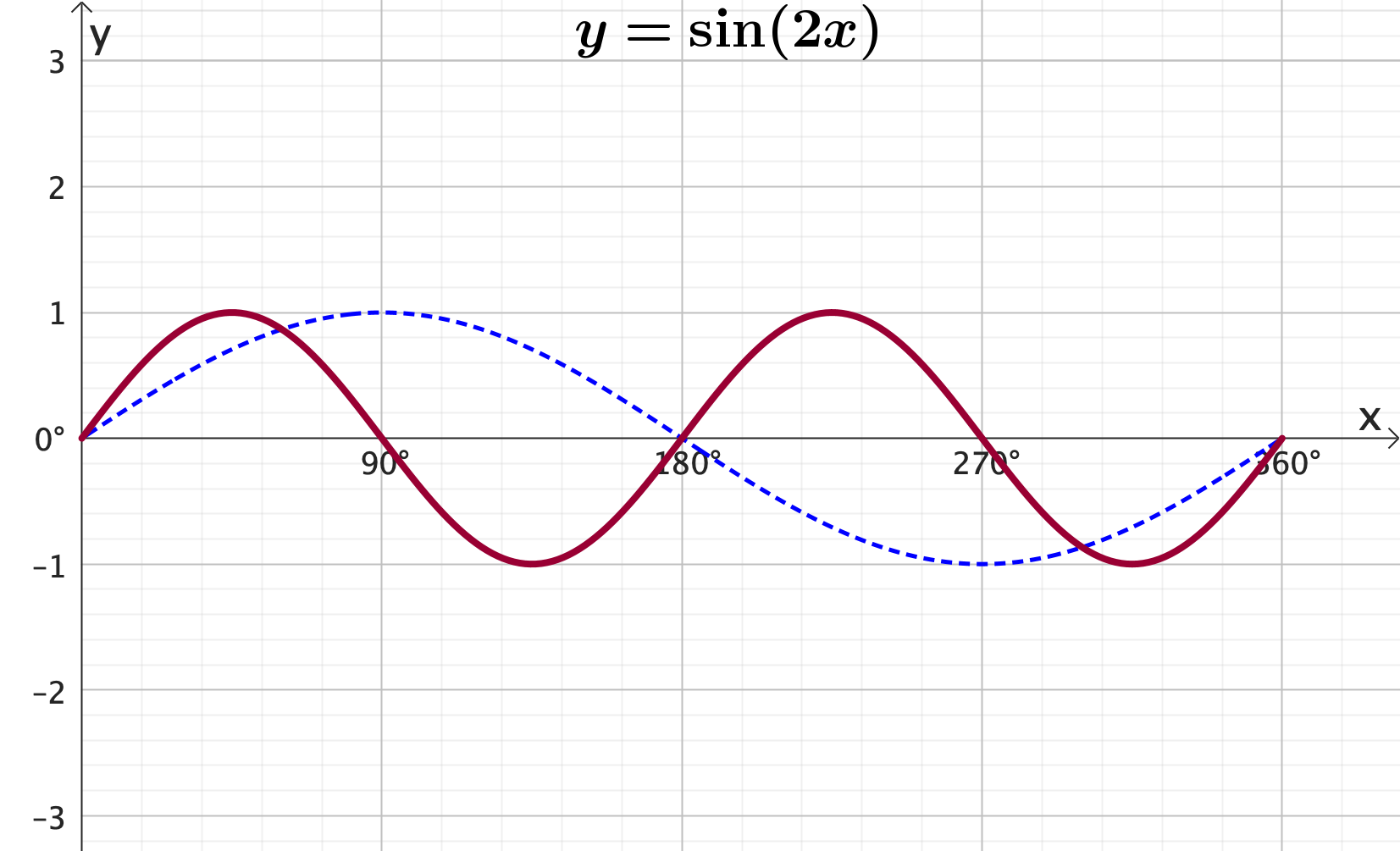
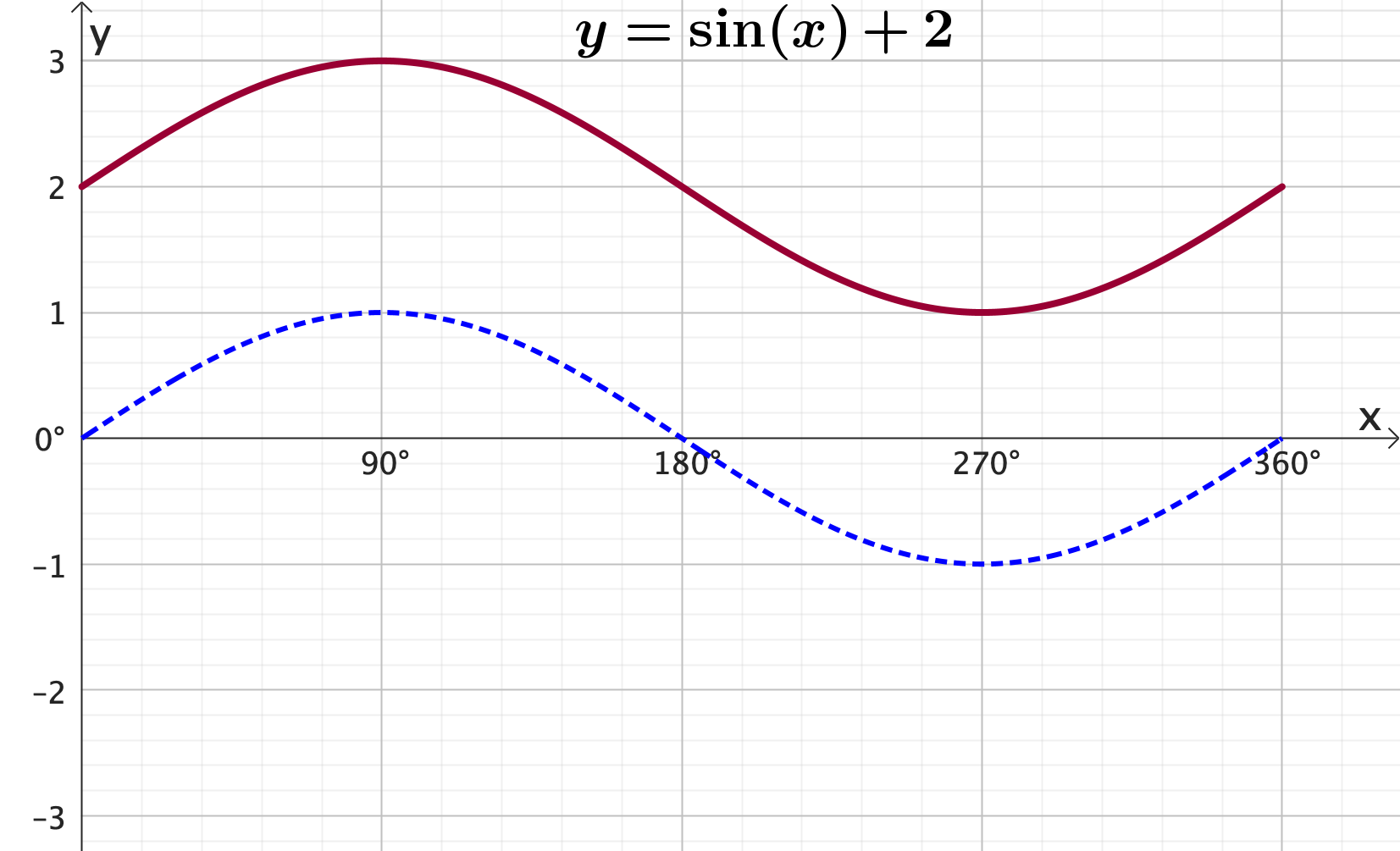
Graphing trigonometric functions: Vertical shift
Graphing trigonometric functions: Vertical shift
Graphing trigonometric functions: Horizontal shift
Graphing trigonometric functions: Horizontal shift
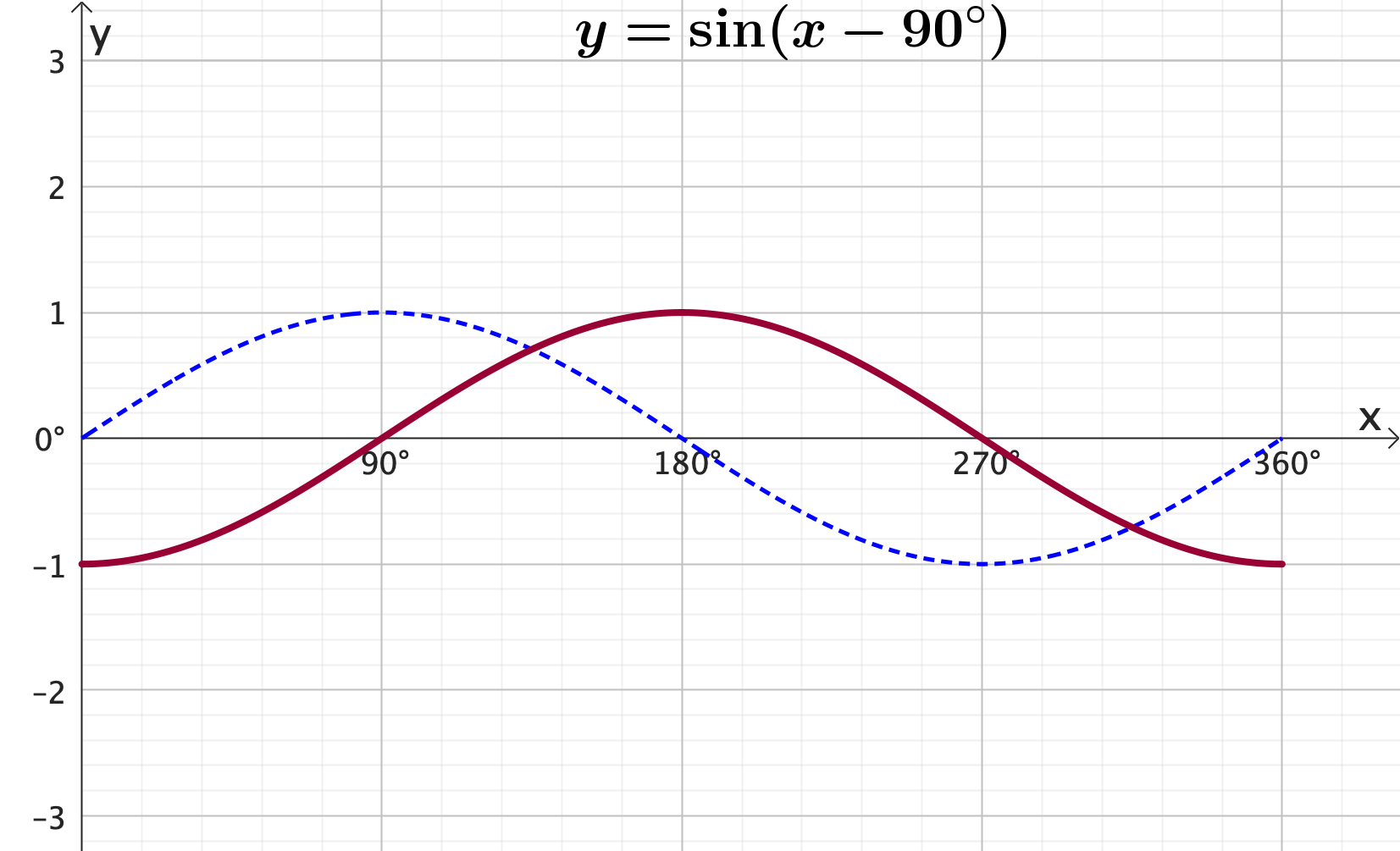
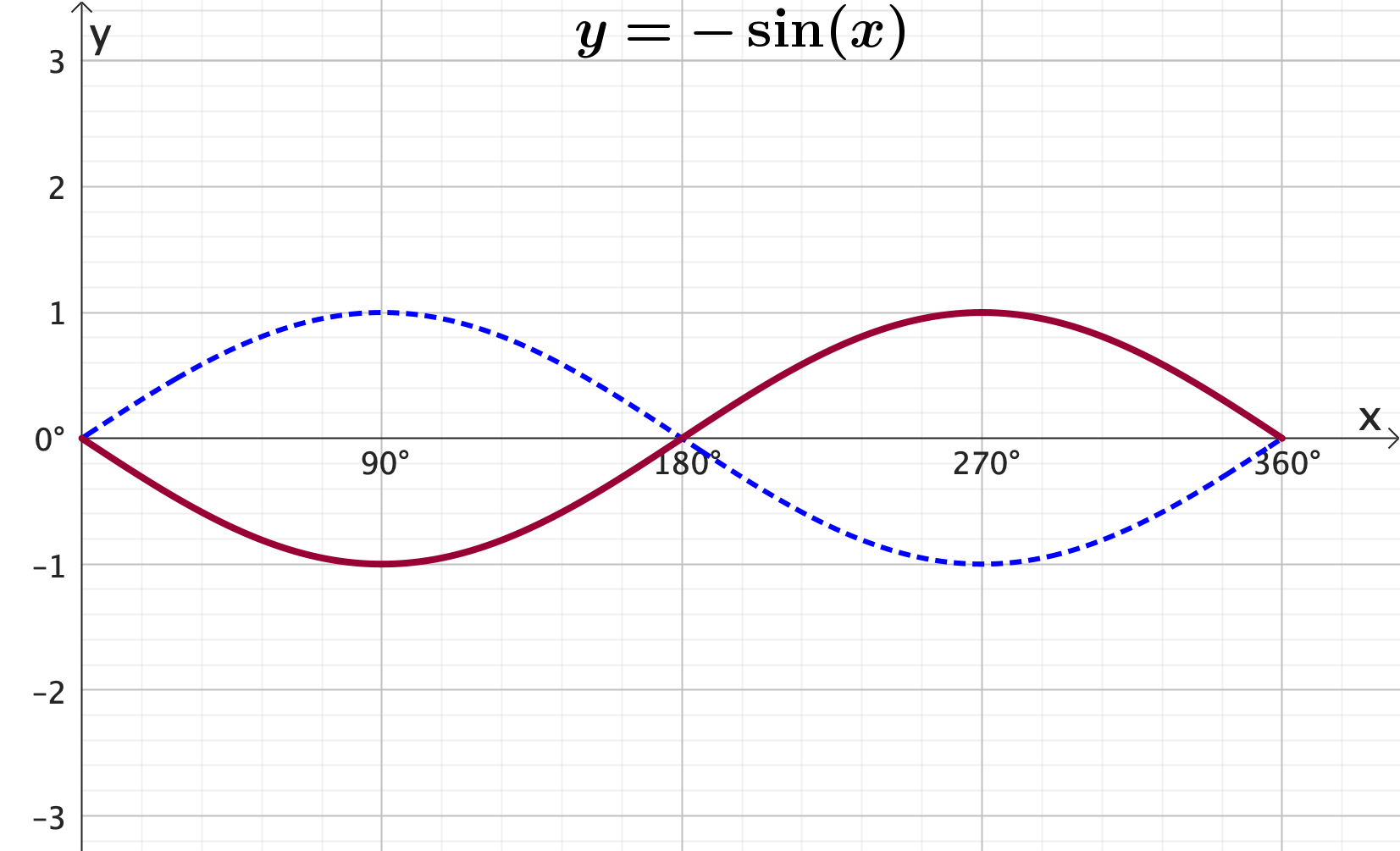
Graphing trigonometric functions: Reflection
Graphing trigonometric functions: Reflection
Graphing trigonometric functions: cos
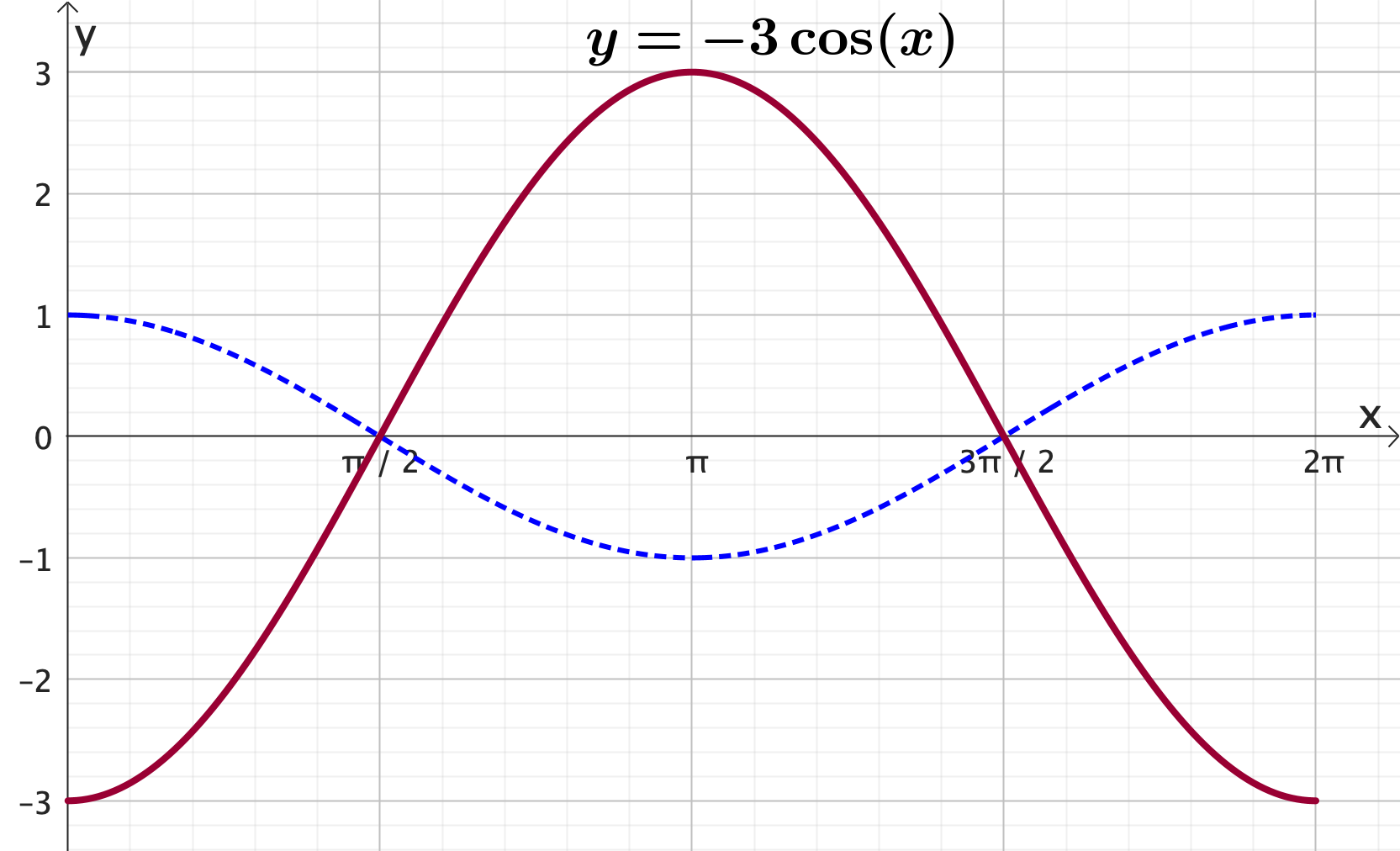
Graphing trigonometric functions: cos - Amplitude
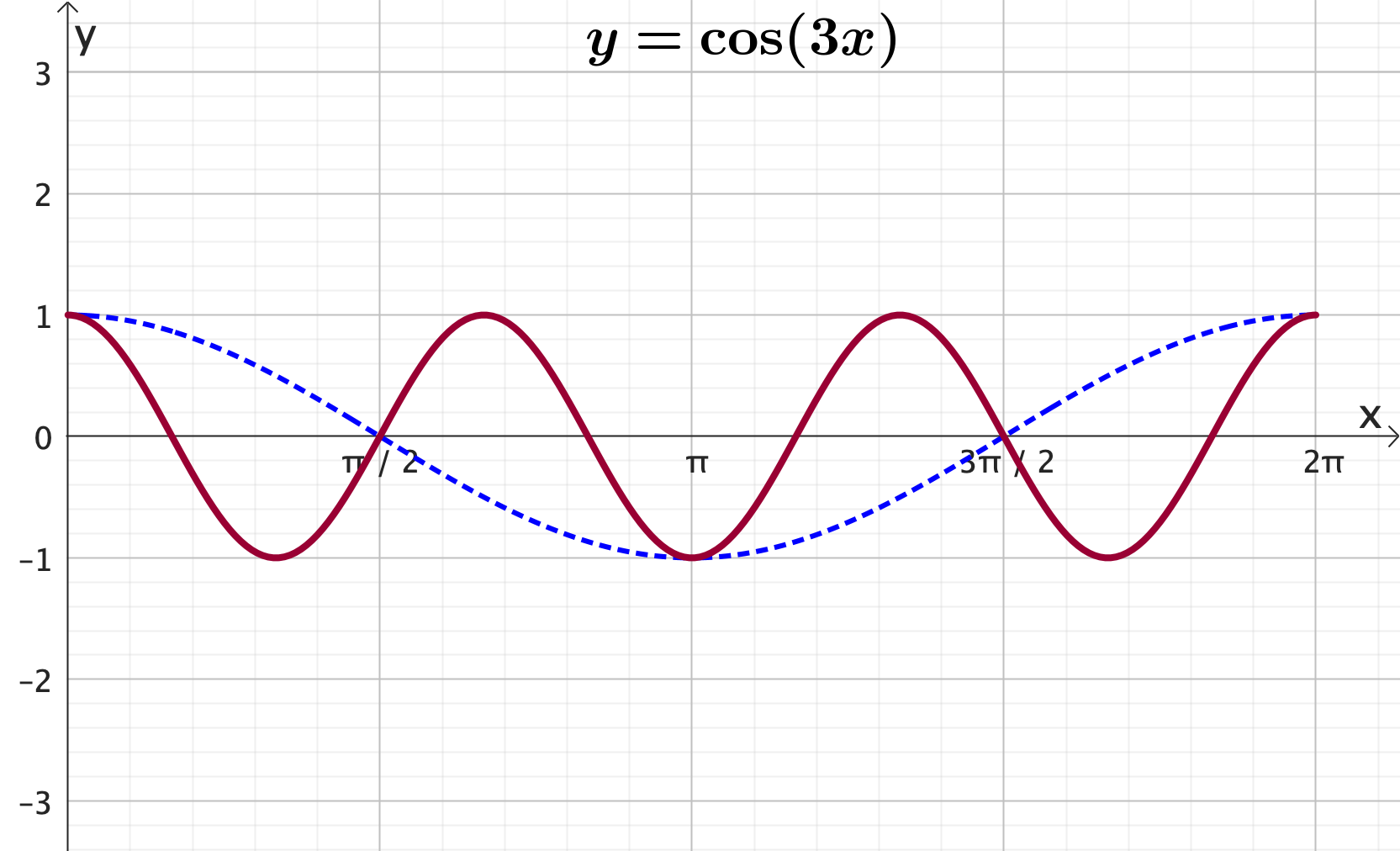
Graphing trigonometric functions: cos - Frequency
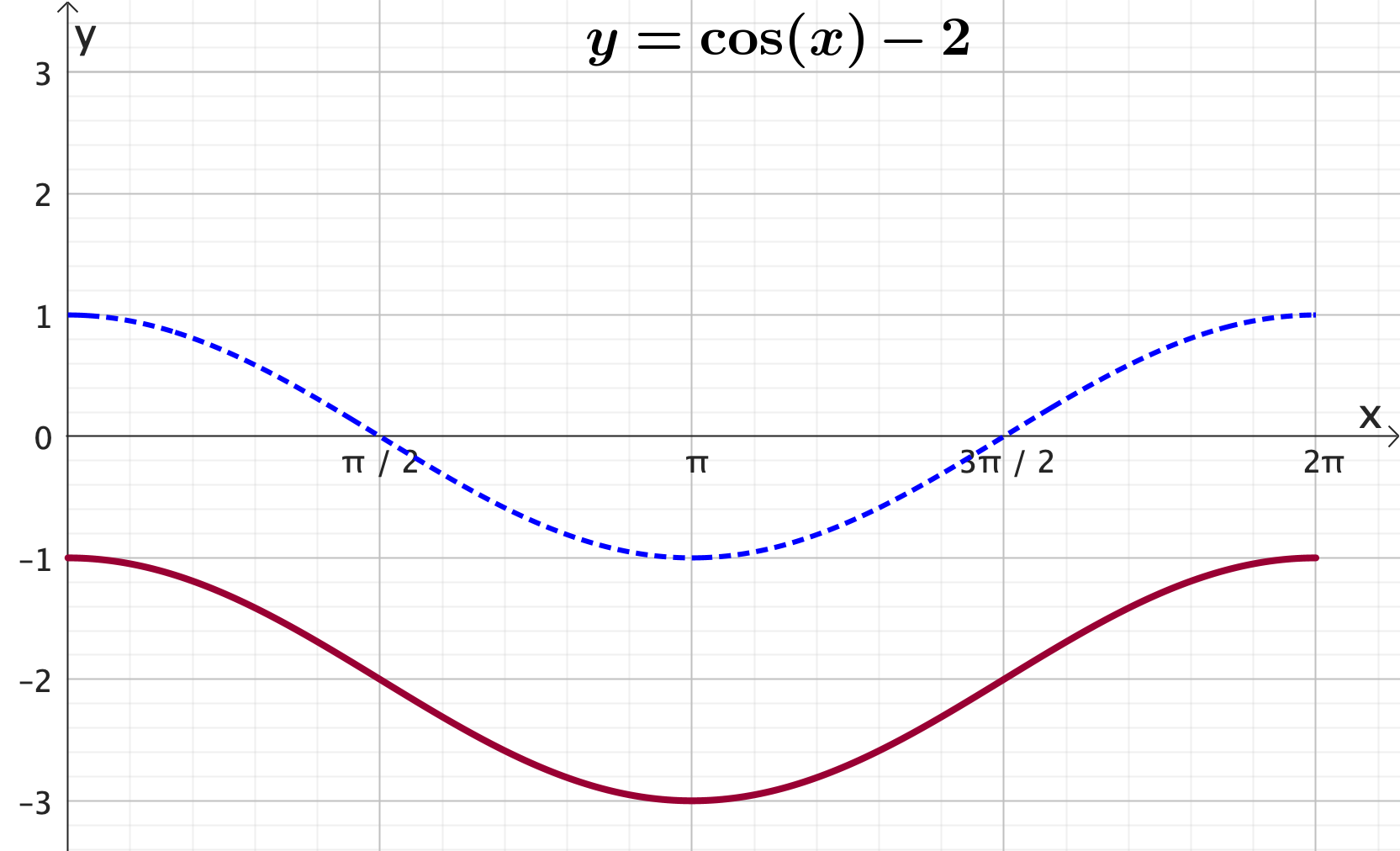
Graphing trigonometric functions: cos - Vertical shift
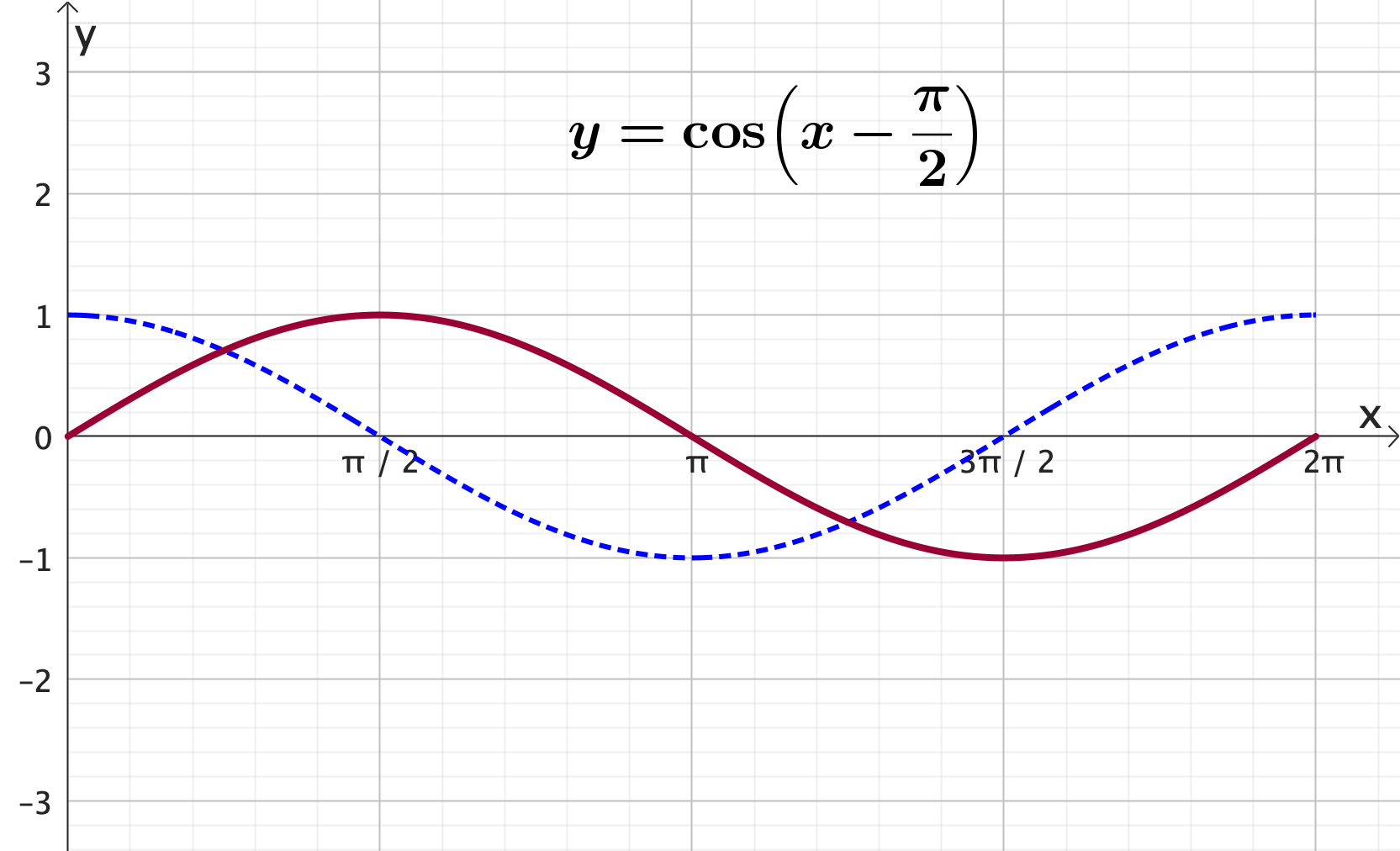
Graphing trigonometric functions: cos - Horizontal shift
Putting all together
$ y = A \sin \big[B\left(x+C\right)\big] + D \;$ or $\; y = A \cos \big[B\left(x+C\right)\big] + D $
- Amplitude is $A$
- Period is $\dfrac{360^\circ}{B}$ or $\dfrac{2\pi}{B}$ (horizontal compression)
- Horizontal shift is $C$ (phase shift)
- Vertical shift is $D$
Example 1: $\;y = 2 \cos(x) -3$
Example 2: $\;y = 3 \sin(x) +1$
Example 3: Find the main features of the plot
Example 4: Find the main features of the plot
Explore more in Desmos
Why do we study trigonometric functions?

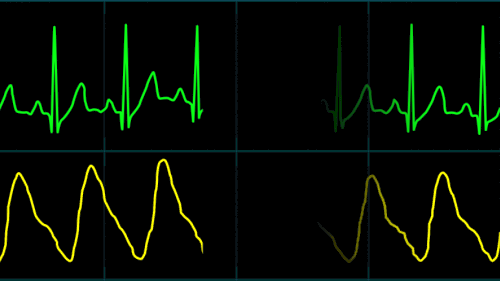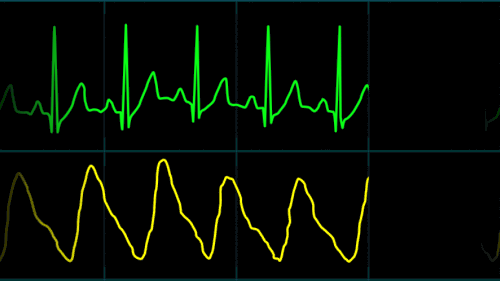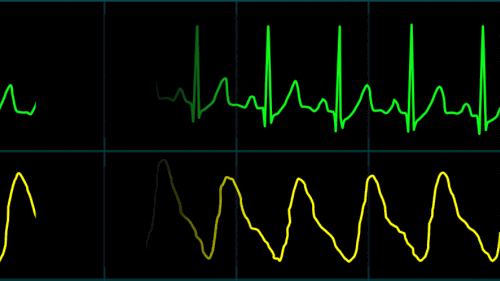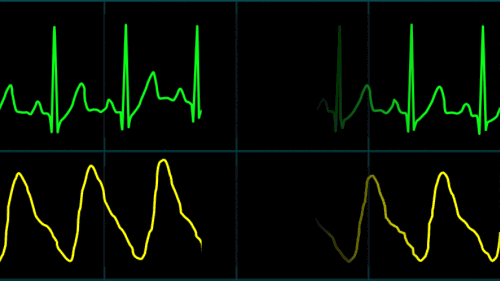
Heart Rate & O2 Saturation graphs
Computer Graphics: Procedural Landscape Generation
\[ f(\mathbf{x}) = \sum_{i=0}^{N-1} A_i \cdot \big[\cos\left(2\pi \, \mathbf{k}_i \cdot \mathbf{x} + \phi_i\right) + \sin\left(2\pi \, \mathbf{k}_i \cdot \mathbf{x} + \theta_i\right)\big] \]
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scans
Sound Processing
Limits
Consider the function \(f(x)=\dfrac{1}{x}\,\) near $\,x=0.$
Limits
Consider the function \(f(x)=\dfrac{\sin (x)}{x}\,\) near $\,x=0.$
Limits: Area under a curve
\(\ds \int_I f(x)dx = \lim \sum_{i=1}^{n} f(x_i^*)(x_i-x_{i-1}) \)
Limits: Tangent line to curve
Estimating a limit numerically
|
Calculate \[\ds\lim_{x\rightarrow 1}\frac{x^2-1}{x-1}\] |
|
Estimating a limit numerically
|
|
|
Finding the limit analytically 🤓
|
Our goal is to prove that: \[\ds\lim_{x\rightarrow 1}\frac{x^2-1}{x-1}=2\] 
|
|
Examples
1. $\,\ds \lim_{x\ra 1}(4x+3)$
2. $\,\ds \lim_{x\ra 1}5x^2$
Example 3
$\ds \lim_{x\ra -2}\frac{x^2+7x+10}{x+2}$
Example 4
$\ds \lim_{x\ra 10}\frac{x^2-100}{x-10}$
Continuity of functions (Intuitive notion)
Continuity of functions (Intuitive notion)
Definition of Continuity
For the function $f(x)$ to be continuous at $x=a,$ it must satisfy the following three criteria:
- $f(a)$ must exist.
- $\ds \lim_{x\ra a} f(x)$ must exist,
- $\ds \lim_{x\ra a} f(x)= f(a).$